Improve your health
Improve your health
Improve your health
12. November 2025
Neuroadaptive Algorithms for Lasting Behavior Change


Neuroadaptive algorithms combine neuroscience and AI to create systems that adjust to your mental and emotional states in real time, helping you form better habits and manage stress. These algorithms use data from brain activity, heart rate, and other physiological signals to provide tailored feedback and guidance. Unlike traditional methods, they respond dynamically to your current needs, ensuring that recommendations are neither too overwhelming nor too simplistic.
Key Points:
Real-Time Feedback: Systems adjust based on brain and body signals, offering timely suggestions like stress management techniques or simplified tasks.
Habit Formation: By monitoring cognitive load, these systems make it easier to adopt and maintain healthy routines.
Closed-Loop Systems: Continuous monitoring ensures interventions evolve with your behavior and preferences.
Applications: Tools like Healify use neuroadaptive algorithms to provide personalized health coaching, improving hydration, sleep, and stress management.
Challenges:
Privacy: Handling sensitive neural and physiological data requires strict safeguards.
Scalability: Making these systems accessible and effective for diverse populations remains difficult.
Neuroadaptive algorithms represent a shift toward more personalized, responsive health tools, but their success depends on addressing privacy concerns and ensuring long-term effectiveness.
Motor Rehabilitation with BCI - Lecture from The BCI & Neurotechnology Spring School 2020
How Neuroadaptive Algorithms Work
Neuroadaptive algorithms use real-time neural and physiological data to create personalized interventions that adapt to your specific needs as they arise.
BCIs and Sensor Technologies
At the core of neuroadaptive systems are brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and physiological sensors, which track your mental and physical state. BCIs, often using non-invasive methods like EEG, measure electrical activity in the brain. Meanwhile, physiological sensors monitor factors like heart rate variability, skin conductance, and breathing patterns. Together, these tools allow algorithms to identify patterns linked to cognitive workload, stress levels, or engagement. For instance, certain EEG patterns combined with changes in heart rate can signal heightened stress or mental effort. Passive BCIs take this a step further by decoding cognitive and emotional states without requiring active input, enabling continuous system adjustments.
Thanks to modern wearables - like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized EEG headsets - gathering this data has become more convenient. By combining neural, physiological, behavioral, and contextual information, neuroadaptive systems gain a comprehensive understanding of your state. This real-time data collection enables systems to make quick, informed adjustments, paving the way for dynamic interactions.
Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Systems
Neuroadaptive systems can operate as either open-loop or closed-loop, depending on how they process data and adapt.
Open-loop systems rely on pre-set responses based on an initial assessment. For example, a fitness app might send the same reminder every day, regardless of your current activity level or mood.
Closed-loop systems continuously monitor your state and adjust in real time, creating a feedback loop. These systems can simplify tasks when you’re overwhelmed or provide more challenging guidance when you’re highly engaged.
System Type | Data Processing | Adaptation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Open-Loop | Initial assessment only | Pre-programmed | Standard app notifications |
Closed-Loop | Continuous monitoring | Real-time adjustments |
Closed-loop systems are particularly effective at enhancing engagement and learning by tailoring their responses to your current state. Over time, these systems become even more personalized by building long-term user profiles.
Building Long-Term User Profiles
Beyond reacting to immediate data, neuroadaptive algorithms refine their understanding of you over time. By analyzing repeated interactions, they develop a detailed user profile that captures not only your current state but also long-term patterns in behavior, preferences, and values. This allows the system to predict your needs and provide more effective support.
For example, the system might learn that you prefer gentle encouragement in the morning but respond better to direct, actionable advice in the evening. Research in this area focuses on creating advanced user models that can anticipate challenges and offer proactive solutions. These evolving profiles ensure that your digital health coach stays relevant and continues to meet your needs as they change over time.
Cognitive Load Optimization in Practice
Neuroadaptive algorithms take the theoretical understanding of cognitive load and turn it into practical, targeted health interventions. These systems ensure health recommendations are delivered at moments when users are most receptive, avoiding the risk of overwhelming them. This approach lays the groundwork for meaningful health improvements by aligning interventions with users' mental readiness.
Research on Cognitive Load and Behavior Change
Studies have found that cognitive load plays a major role in whether people adopt and stick to new habits. When the brain is overloaded - due to stress or processing too much information - it's much harder to maintain healthy behaviors. Neuroadaptive systems tackle this by adjusting interventions in real time, keeping cognitive load in a manageable range. This approach helps users stay engaged and build habits more effectively [4][5].
Dynamic Adjustments Based on Real-Time Data
Using real-time data, these algorithms actively manage cognitive load. Sensors like EEG, heart rate variability monitors, and skin conductance trackers allow systems to adapt intervention timing, complexity, and frequency. For instance, if stress levels spike, the system might delay non-urgent recommendations or simplify its suggestions [4][3].
One study highlighted a neuroadaptive haptics system that used reinforcement learning to adjust feedback in virtual reality. By combining explicit user ratings with neural signals, the system reduced cognitive load while improving user immersion [4][5].
In health coaching platforms like Healify, this adaptability is applied in everyday scenarios. If the system detects dehydration, it might suggest something simple like "replenish with electrolytes." On a low-activity day, it could recommend a short, manageable walk instead of a high-intensity workout [1].
Evidence of Improved User Engagement
Research shows that neuroadaptive systems, powered by reinforcement learning and EEG-based neural decoders, lead to better task performance and accurate cognitive state tracking. For example, a 2025 study on a neuroadaptive BCI-based system in a virtual reality motor learning program reported improved task outcomes and effective EEG modulation - all while keeping user discomfort minimal [8]. Similarly, the Neuro-Informed Adaptive Learning (NIAL) algorithm excelled in real-time cardiovascular monitoring, outperforming traditional deep learning models by dynamically adjusting based on user performance [8].
These systems succeed because they align interventions with users' internal cognitive and emotional states - not just their observable actions. This personalized approach proves far more effective than generic, one-size-fits-all strategies. By respecting natural cognitive rhythms, neuroadaptive systems create smoother, more intuitive interactions that encourage lasting behavior changes [8][2].
Applications in Health Coaching
Neuroadaptive algorithms are changing the game in health coaching by offering real-time, personalized recommendations. Instead of relying on generic advice, these systems analyze physiological data to provide guidance tailored to each individual’s current state and needs.
Supporting Habit Formation and Daily Routines
One of the standout benefits of neuroadaptive algorithms is their ability to help users build and maintain healthy habits. By monitoring factors like cognitive load, stress levels, and energy patterns, these systems can time their prompts for moments when users are most likely to act. For instance, if someone is mentally drained, the algorithm might hold off on non-urgent suggestions or simplify its advice to avoid overwhelming them.
What sets these systems apart is their ability to adapt. Unlike static reminders that show up at the same time every day, neuroadaptive systems learn and adjust to personal routines. They can identify the best times to nudge users toward habits like exercising or staying hydrated. Studies have shown that such tailored approaches can boost adherence to health routines by as much as 30% compared to standard, one-size-fits-all methods [5]. In health coaching, this means daily prompts evolve alongside the user’s changing preferences and behaviors, making the guidance more effective over time.
Real-Time Stress and Sleep Management
Managing stress and improving sleep are two areas where neuroadaptive health coaching truly shines. These systems use data like heart rate variability and skin conductance to detect when stress levels rise, offering timely interventions. For example, if stress spikes, the algorithm might suggest a quick breathing exercise or recommend lightening the day's schedule to reduce pressure.
When it comes to sleep, neuroadaptive tools go beyond basic tracking. They analyze sleep stages and environmental factors to provide actionable advice tailored to the individual. This could mean suggesting an earlier bedtime, adjusting room conditions, or incorporating mindfulness exercises into a nightly routine. By addressing these factors in real time, these systems integrate seamlessly into broader health coaching plans, helping users maintain overall well-being.
Case Study: Healify and Neuroadaptive Health Coaching
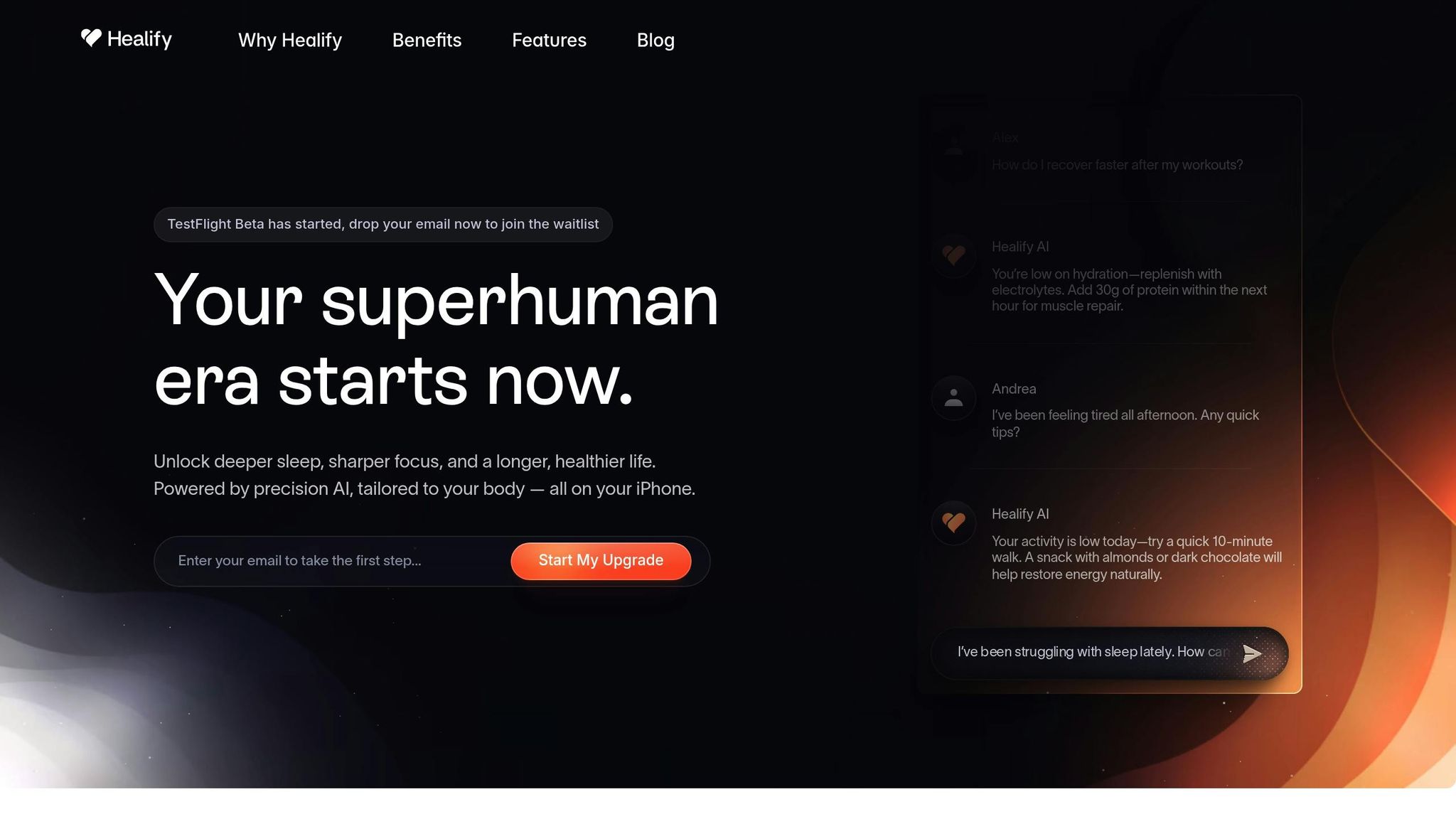
Healify offers a practical example of how neuroadaptive algorithms work in health coaching. Its AI health coach, Anna, uses data from wearables, biometrics, bloodwork, and lifestyle inputs to deliver round-the-clock, personalized guidance. The platform excels at turning complex data into simple, actionable steps.
For instance, if a user asks, "How can I recover faster after workouts?" Anna might respond with advice like, "You're low on hydration - replenish with electrolytes. Add 30g of protein within the next hour to support muscle repair." Or, if someone reports feeling tired, Anna could analyze their activity levels and suggest, "Your activity is low today - try a quick 10-minute walk. A snack with almonds or dark chocolate can help restore your energy naturally" [1].
Healify also monitors stress indicators, such as cortisol levels, to provide immediate feedback. For example, a user might receive an alert like, "Peak Cortisol: 250 nmol/L. Stress detected. Try a short meditation session or take a walk outside." These real-time insights empower users to make adjustments that improve their overall health.
The feedback from users underscores the impact of this approach:
"Finally, my health data makes sense. I know exactly what to do to feel better." - Sarah L, Founder [1]
Future Opportunities and Challenges
The field of neuroadaptive algorithms is advancing rapidly, bringing developments that could reshape how we approach behavior change. However, several hurdles must be addressed before these technologies can fully deliver on their promise.
Emerging Trends in Neuroadaptive AI
One of the most promising advancements is the integration of reinforcement learning (RL) into neuroadaptive systems. Recent studies show that RL agents, when paired with EEG decoders, can achieve mean F1 scores of 0.8 in classifying user experiences [4]. This means these systems can adapt to real-time brain signals instead of relying solely on explicit feedback from users.
The combination of extended reality (XR) and virtual reality (VR) is also opening up new possibilities. These immersive environments can adjust sensory feedback, task difficulty, or content based on users’ real-time mental states [4][5][7]. Early applications include adaptive meditation tools, phobia exposure therapy, and personalized training systems. For example, a neuroadaptive haptics system using EEG data can tailor feedback in XR environments, enhancing the user's sense of immersion while lowering cognitive strain [4].
Another emerging area is the focus on ethically designed AI. Developers are working to create systems that align with users’ personal values and experiences [2][4]. This includes neuroadaptive chatbots capable of recognizing the moral weight of interactions and modifying their tone for sensitive topics [3]. Additionally, the formation of the Society for Neuroadaptive Technology, led by researchers at Brandenburg University of Technology and Zander Labs, reflects growing institutional efforts to standardize and advance these technologies [2].
While these advancements are exciting, they also highlight the practical challenges that lie ahead.
Challenges in Data Privacy and Scalability
Despite technological progress, data privacy remains a major concern. Handling sensitive neural and physiological data requires strict adherence to U.S. privacy laws like HIPAA, along with robust encryption and transparent data practices [2]. The collection and use of brain and biometric data raise critical questions about consent, ownership, and potential misuse. The recent surge in patents for brain-computer interface technologies underscores the commercial interest in this area, but also amplifies concerns about protecting such intimate information [3].
Scalability is another significant challenge. Developing algorithms that can adapt to the physiological, cognitive, and cultural diversity across the U.S. population requires extensive research and development [2]. Beyond that, these systems must be affordable and user-friendly to move from research labs into everyday settings. Real-time applications face additional difficulties, as both explicit and implicit rewards often introduce noise into training data, complicating RL model convergence [4].
Open Questions for Future Research
To ensure the long-term success of neuroadaptive health coaching, several pressing questions need answers. For instance, the long-term effectiveness of these interventions remains unclear. While initial results are promising, there is limited longitudinal data on their sustained impact and how user engagement evolves over time [2][3].
Another key challenge lies in the integration of neuroadaptive algorithms with mainstream health platforms. Seamless integration will require robust consent mechanisms and strong privacy protections to meet user expectations.
The field is also exploring single-trial mental state decoding, where milliseconds of EEG data can reveal mental states in response to text stimuli. While progress has been made, decoding accuracy still needs improvement before these systems can be practically deployed [3].
Finally, addressing algorithmic bias and user autonomy is critical. Ensuring these systems are free from bias while preserving users’ control over their experiences is essential [2]. Experts recommend starting with pilot studies in controlled environments to validate neuroadaptive approaches. They also stress the importance of prioritizing privacy, ethical design, and forming interdisciplinary teams that include neuroscientists, AI experts, ethicists, and healthcare professionals [2].
Striking the right balance between innovation and responsibility will be crucial to ensuring these technologies serve users effectively while safeguarding their privacy and autonomy.
Conclusion
Neuroadaptive algorithms are reshaping how we approach behavior change by moving away from rigid, one-size-fits-all methods. Instead, they use closed-loop systems that adapt in real time to a user's cognitive and emotional states, consistently delivering better outcomes compared to static approaches [4][6][8]. These systems don’t force users to fit into predefined molds; they evolve by recognizing individual patterns, values, and shifting needs, paving the way for sustainable and meaningful changes.
A clear example of this is Healify, which leverages data from wearables, biometrics, and lifestyle inputs to provide tailored health coaching. By adapting to each user’s unique circumstances, Healify highlights the growing shift toward neuroadaptive, data-driven solutions in health and wellness.
The combination of passive Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and reinforcement learning is pushing the boundaries of personalized health coaching even further [3]. These tools allow for continuous, subtle monitoring of cognitive and emotional states without requiring direct user input, leading to interventions that are more precise and responsive.
Prof. Dr. Thorsten O. Zander’s research showcases how neuroadaptive technologies enable AI systems to better align with individual needs [8]. Meanwhile, the $30 million investment in the NAFAS project and the release of new patents signal increasing commercial interest and the transformative possibilities of this field [8][9].
Moving forward, success will hinge on balancing innovation with ethical responsibility. Challenges like safeguarding data privacy, ensuring scalability, and maintaining algorithmic transparency remain significant. However, the potential of co-adaptive, trustworthy, and ethically sound health coaching systems makes tackling these issues a necessary step toward progress.
FAQs
How do neuroadaptive algorithms protect sensitive neural and physiological data?
Neuroadaptive algorithms prioritize privacy and security from the ground up. They rely on advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive information, ensuring data remains secure whether it's being stored or transmitted. On top of that, these systems frequently anonymize or combine data, making it nearly impossible to trace back to individual users.
By following rigorous data privacy laws and regulations, these algorithms not only safeguard user information but also build trust. This approach allows them to deliver tailored, effective solutions for influencing behavior while respecting personal boundaries.
Why are closed-loop systems more effective than open-loop systems for real-time user adaptation?
Closed-loop systems stand out because they constantly track user behavior and feedback, enabling real-time adjustments. Unlike open-loop systems that stick to a fixed method, closed-loop systems use real-world data to fine-tune their approach, delivering a more tailored and effective experience.
Take neuroadaptive algorithms as an example. These systems can assess a user's cognitive load and make immediate changes to maintain engagement without causing fatigue. This ability to adapt on the fly makes closed-loop systems particularly useful for driving long-term behavior changes and achieving better results over time.
How do neuroadaptive algorithms help manage cognitive load to support lasting habit formation and behavior change?
Neuroadaptive algorithms use real-time data to fine-tune and customize the cognitive challenges individuals face while building new habits. By adjusting to your mental state on the fly, these algorithms strike the perfect balance - keeping tasks or suggestions challenging enough to promote growth but not so difficult that they feel overwhelming.
This dynamic approach helps maintain motivation and keeps users engaged, making it smoother to develop healthier habits over time. For instance, apps like Healify harness these advanced algorithms to deliver tailored insights and practical steps, supporting users in achieving lasting improvements in both physical and mental health.
Related Blog Posts
Neuroadaptive algorithms combine neuroscience and AI to create systems that adjust to your mental and emotional states in real time, helping you form better habits and manage stress. These algorithms use data from brain activity, heart rate, and other physiological signals to provide tailored feedback and guidance. Unlike traditional methods, they respond dynamically to your current needs, ensuring that recommendations are neither too overwhelming nor too simplistic.
Key Points:
Real-Time Feedback: Systems adjust based on brain and body signals, offering timely suggestions like stress management techniques or simplified tasks.
Habit Formation: By monitoring cognitive load, these systems make it easier to adopt and maintain healthy routines.
Closed-Loop Systems: Continuous monitoring ensures interventions evolve with your behavior and preferences.
Applications: Tools like Healify use neuroadaptive algorithms to provide personalized health coaching, improving hydration, sleep, and stress management.
Challenges:
Privacy: Handling sensitive neural and physiological data requires strict safeguards.
Scalability: Making these systems accessible and effective for diverse populations remains difficult.
Neuroadaptive algorithms represent a shift toward more personalized, responsive health tools, but their success depends on addressing privacy concerns and ensuring long-term effectiveness.
Motor Rehabilitation with BCI - Lecture from The BCI & Neurotechnology Spring School 2020
How Neuroadaptive Algorithms Work
Neuroadaptive algorithms use real-time neural and physiological data to create personalized interventions that adapt to your specific needs as they arise.
BCIs and Sensor Technologies
At the core of neuroadaptive systems are brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and physiological sensors, which track your mental and physical state. BCIs, often using non-invasive methods like EEG, measure electrical activity in the brain. Meanwhile, physiological sensors monitor factors like heart rate variability, skin conductance, and breathing patterns. Together, these tools allow algorithms to identify patterns linked to cognitive workload, stress levels, or engagement. For instance, certain EEG patterns combined with changes in heart rate can signal heightened stress or mental effort. Passive BCIs take this a step further by decoding cognitive and emotional states without requiring active input, enabling continuous system adjustments.
Thanks to modern wearables - like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized EEG headsets - gathering this data has become more convenient. By combining neural, physiological, behavioral, and contextual information, neuroadaptive systems gain a comprehensive understanding of your state. This real-time data collection enables systems to make quick, informed adjustments, paving the way for dynamic interactions.
Open-Loop vs. Closed-Loop Systems
Neuroadaptive systems can operate as either open-loop or closed-loop, depending on how they process data and adapt.
Open-loop systems rely on pre-set responses based on an initial assessment. For example, a fitness app might send the same reminder every day, regardless of your current activity level or mood.
Closed-loop systems continuously monitor your state and adjust in real time, creating a feedback loop. These systems can simplify tasks when you’re overwhelmed or provide more challenging guidance when you’re highly engaged.
System Type | Data Processing | Adaptation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Open-Loop | Initial assessment only | Pre-programmed | Standard app notifications |
Closed-Loop | Continuous monitoring | Real-time adjustments |
Closed-loop systems are particularly effective at enhancing engagement and learning by tailoring their responses to your current state. Over time, these systems become even more personalized by building long-term user profiles.
Building Long-Term User Profiles
Beyond reacting to immediate data, neuroadaptive algorithms refine their understanding of you over time. By analyzing repeated interactions, they develop a detailed user profile that captures not only your current state but also long-term patterns in behavior, preferences, and values. This allows the system to predict your needs and provide more effective support.
For example, the system might learn that you prefer gentle encouragement in the morning but respond better to direct, actionable advice in the evening. Research in this area focuses on creating advanced user models that can anticipate challenges and offer proactive solutions. These evolving profiles ensure that your digital health coach stays relevant and continues to meet your needs as they change over time.
Cognitive Load Optimization in Practice
Neuroadaptive algorithms take the theoretical understanding of cognitive load and turn it into practical, targeted health interventions. These systems ensure health recommendations are delivered at moments when users are most receptive, avoiding the risk of overwhelming them. This approach lays the groundwork for meaningful health improvements by aligning interventions with users' mental readiness.
Research on Cognitive Load and Behavior Change
Studies have found that cognitive load plays a major role in whether people adopt and stick to new habits. When the brain is overloaded - due to stress or processing too much information - it's much harder to maintain healthy behaviors. Neuroadaptive systems tackle this by adjusting interventions in real time, keeping cognitive load in a manageable range. This approach helps users stay engaged and build habits more effectively [4][5].
Dynamic Adjustments Based on Real-Time Data
Using real-time data, these algorithms actively manage cognitive load. Sensors like EEG, heart rate variability monitors, and skin conductance trackers allow systems to adapt intervention timing, complexity, and frequency. For instance, if stress levels spike, the system might delay non-urgent recommendations or simplify its suggestions [4][3].
One study highlighted a neuroadaptive haptics system that used reinforcement learning to adjust feedback in virtual reality. By combining explicit user ratings with neural signals, the system reduced cognitive load while improving user immersion [4][5].
In health coaching platforms like Healify, this adaptability is applied in everyday scenarios. If the system detects dehydration, it might suggest something simple like "replenish with electrolytes." On a low-activity day, it could recommend a short, manageable walk instead of a high-intensity workout [1].
Evidence of Improved User Engagement
Research shows that neuroadaptive systems, powered by reinforcement learning and EEG-based neural decoders, lead to better task performance and accurate cognitive state tracking. For example, a 2025 study on a neuroadaptive BCI-based system in a virtual reality motor learning program reported improved task outcomes and effective EEG modulation - all while keeping user discomfort minimal [8]. Similarly, the Neuro-Informed Adaptive Learning (NIAL) algorithm excelled in real-time cardiovascular monitoring, outperforming traditional deep learning models by dynamically adjusting based on user performance [8].
These systems succeed because they align interventions with users' internal cognitive and emotional states - not just their observable actions. This personalized approach proves far more effective than generic, one-size-fits-all strategies. By respecting natural cognitive rhythms, neuroadaptive systems create smoother, more intuitive interactions that encourage lasting behavior changes [8][2].
Applications in Health Coaching
Neuroadaptive algorithms are changing the game in health coaching by offering real-time, personalized recommendations. Instead of relying on generic advice, these systems analyze physiological data to provide guidance tailored to each individual’s current state and needs.
Supporting Habit Formation and Daily Routines
One of the standout benefits of neuroadaptive algorithms is their ability to help users build and maintain healthy habits. By monitoring factors like cognitive load, stress levels, and energy patterns, these systems can time their prompts for moments when users are most likely to act. For instance, if someone is mentally drained, the algorithm might hold off on non-urgent suggestions or simplify its advice to avoid overwhelming them.
What sets these systems apart is their ability to adapt. Unlike static reminders that show up at the same time every day, neuroadaptive systems learn and adjust to personal routines. They can identify the best times to nudge users toward habits like exercising or staying hydrated. Studies have shown that such tailored approaches can boost adherence to health routines by as much as 30% compared to standard, one-size-fits-all methods [5]. In health coaching, this means daily prompts evolve alongside the user’s changing preferences and behaviors, making the guidance more effective over time.
Real-Time Stress and Sleep Management
Managing stress and improving sleep are two areas where neuroadaptive health coaching truly shines. These systems use data like heart rate variability and skin conductance to detect when stress levels rise, offering timely interventions. For example, if stress spikes, the algorithm might suggest a quick breathing exercise or recommend lightening the day's schedule to reduce pressure.
When it comes to sleep, neuroadaptive tools go beyond basic tracking. They analyze sleep stages and environmental factors to provide actionable advice tailored to the individual. This could mean suggesting an earlier bedtime, adjusting room conditions, or incorporating mindfulness exercises into a nightly routine. By addressing these factors in real time, these systems integrate seamlessly into broader health coaching plans, helping users maintain overall well-being.
Case Study: Healify and Neuroadaptive Health Coaching

Healify offers a practical example of how neuroadaptive algorithms work in health coaching. Its AI health coach, Anna, uses data from wearables, biometrics, bloodwork, and lifestyle inputs to deliver round-the-clock, personalized guidance. The platform excels at turning complex data into simple, actionable steps.
For instance, if a user asks, "How can I recover faster after workouts?" Anna might respond with advice like, "You're low on hydration - replenish with electrolytes. Add 30g of protein within the next hour to support muscle repair." Or, if someone reports feeling tired, Anna could analyze their activity levels and suggest, "Your activity is low today - try a quick 10-minute walk. A snack with almonds or dark chocolate can help restore your energy naturally" [1].
Healify also monitors stress indicators, such as cortisol levels, to provide immediate feedback. For example, a user might receive an alert like, "Peak Cortisol: 250 nmol/L. Stress detected. Try a short meditation session or take a walk outside." These real-time insights empower users to make adjustments that improve their overall health.
The feedback from users underscores the impact of this approach:
"Finally, my health data makes sense. I know exactly what to do to feel better." - Sarah L, Founder [1]
Future Opportunities and Challenges
The field of neuroadaptive algorithms is advancing rapidly, bringing developments that could reshape how we approach behavior change. However, several hurdles must be addressed before these technologies can fully deliver on their promise.
Emerging Trends in Neuroadaptive AI
One of the most promising advancements is the integration of reinforcement learning (RL) into neuroadaptive systems. Recent studies show that RL agents, when paired with EEG decoders, can achieve mean F1 scores of 0.8 in classifying user experiences [4]. This means these systems can adapt to real-time brain signals instead of relying solely on explicit feedback from users.
The combination of extended reality (XR) and virtual reality (VR) is also opening up new possibilities. These immersive environments can adjust sensory feedback, task difficulty, or content based on users’ real-time mental states [4][5][7]. Early applications include adaptive meditation tools, phobia exposure therapy, and personalized training systems. For example, a neuroadaptive haptics system using EEG data can tailor feedback in XR environments, enhancing the user's sense of immersion while lowering cognitive strain [4].
Another emerging area is the focus on ethically designed AI. Developers are working to create systems that align with users’ personal values and experiences [2][4]. This includes neuroadaptive chatbots capable of recognizing the moral weight of interactions and modifying their tone for sensitive topics [3]. Additionally, the formation of the Society for Neuroadaptive Technology, led by researchers at Brandenburg University of Technology and Zander Labs, reflects growing institutional efforts to standardize and advance these technologies [2].
While these advancements are exciting, they also highlight the practical challenges that lie ahead.
Challenges in Data Privacy and Scalability
Despite technological progress, data privacy remains a major concern. Handling sensitive neural and physiological data requires strict adherence to U.S. privacy laws like HIPAA, along with robust encryption and transparent data practices [2]. The collection and use of brain and biometric data raise critical questions about consent, ownership, and potential misuse. The recent surge in patents for brain-computer interface technologies underscores the commercial interest in this area, but also amplifies concerns about protecting such intimate information [3].
Scalability is another significant challenge. Developing algorithms that can adapt to the physiological, cognitive, and cultural diversity across the U.S. population requires extensive research and development [2]. Beyond that, these systems must be affordable and user-friendly to move from research labs into everyday settings. Real-time applications face additional difficulties, as both explicit and implicit rewards often introduce noise into training data, complicating RL model convergence [4].
Open Questions for Future Research
To ensure the long-term success of neuroadaptive health coaching, several pressing questions need answers. For instance, the long-term effectiveness of these interventions remains unclear. While initial results are promising, there is limited longitudinal data on their sustained impact and how user engagement evolves over time [2][3].
Another key challenge lies in the integration of neuroadaptive algorithms with mainstream health platforms. Seamless integration will require robust consent mechanisms and strong privacy protections to meet user expectations.
The field is also exploring single-trial mental state decoding, where milliseconds of EEG data can reveal mental states in response to text stimuli. While progress has been made, decoding accuracy still needs improvement before these systems can be practically deployed [3].
Finally, addressing algorithmic bias and user autonomy is critical. Ensuring these systems are free from bias while preserving users’ control over their experiences is essential [2]. Experts recommend starting with pilot studies in controlled environments to validate neuroadaptive approaches. They also stress the importance of prioritizing privacy, ethical design, and forming interdisciplinary teams that include neuroscientists, AI experts, ethicists, and healthcare professionals [2].
Striking the right balance between innovation and responsibility will be crucial to ensuring these technologies serve users effectively while safeguarding their privacy and autonomy.
Conclusion
Neuroadaptive algorithms are reshaping how we approach behavior change by moving away from rigid, one-size-fits-all methods. Instead, they use closed-loop systems that adapt in real time to a user's cognitive and emotional states, consistently delivering better outcomes compared to static approaches [4][6][8]. These systems don’t force users to fit into predefined molds; they evolve by recognizing individual patterns, values, and shifting needs, paving the way for sustainable and meaningful changes.
A clear example of this is Healify, which leverages data from wearables, biometrics, and lifestyle inputs to provide tailored health coaching. By adapting to each user’s unique circumstances, Healify highlights the growing shift toward neuroadaptive, data-driven solutions in health and wellness.
The combination of passive Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and reinforcement learning is pushing the boundaries of personalized health coaching even further [3]. These tools allow for continuous, subtle monitoring of cognitive and emotional states without requiring direct user input, leading to interventions that are more precise and responsive.
Prof. Dr. Thorsten O. Zander’s research showcases how neuroadaptive technologies enable AI systems to better align with individual needs [8]. Meanwhile, the $30 million investment in the NAFAS project and the release of new patents signal increasing commercial interest and the transformative possibilities of this field [8][9].
Moving forward, success will hinge on balancing innovation with ethical responsibility. Challenges like safeguarding data privacy, ensuring scalability, and maintaining algorithmic transparency remain significant. However, the potential of co-adaptive, trustworthy, and ethically sound health coaching systems makes tackling these issues a necessary step toward progress.
FAQs
How do neuroadaptive algorithms protect sensitive neural and physiological data?
Neuroadaptive algorithms prioritize privacy and security from the ground up. They rely on advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive information, ensuring data remains secure whether it's being stored or transmitted. On top of that, these systems frequently anonymize or combine data, making it nearly impossible to trace back to individual users.
By following rigorous data privacy laws and regulations, these algorithms not only safeguard user information but also build trust. This approach allows them to deliver tailored, effective solutions for influencing behavior while respecting personal boundaries.
Why are closed-loop systems more effective than open-loop systems for real-time user adaptation?
Closed-loop systems stand out because they constantly track user behavior and feedback, enabling real-time adjustments. Unlike open-loop systems that stick to a fixed method, closed-loop systems use real-world data to fine-tune their approach, delivering a more tailored and effective experience.
Take neuroadaptive algorithms as an example. These systems can assess a user's cognitive load and make immediate changes to maintain engagement without causing fatigue. This ability to adapt on the fly makes closed-loop systems particularly useful for driving long-term behavior changes and achieving better results over time.
How do neuroadaptive algorithms help manage cognitive load to support lasting habit formation and behavior change?
Neuroadaptive algorithms use real-time data to fine-tune and customize the cognitive challenges individuals face while building new habits. By adjusting to your mental state on the fly, these algorithms strike the perfect balance - keeping tasks or suggestions challenging enough to promote growth but not so difficult that they feel overwhelming.
This dynamic approach helps maintain motivation and keeps users engaged, making it smoother to develop healthier habits over time. For instance, apps like Healify harness these advanced algorithms to deliver tailored insights and practical steps, supporting users in achieving lasting improvements in both physical and mental health.
Related Blog Posts
Endlich die Kontrolle über Ihre Gesundheit übernehmen

Endlich die Kontrolle über Ihre Gesundheit übernehmen

Endlich die Kontrolle über Ihre Gesundheit übernehmen





