Improve your health
Improve your health
Improve your health
20. Januar 2026
AI-Powered Sleep Disorder Detection: How It Works


AI is transforming sleep health by offering faster, more accessible ways to detect sleep disorders. Traditionally, diagnosing conditions like sleep apnea or insomnia required overnight lab tests with complex equipment, which are expensive and inconvenient. Now, AI-driven systems use non-contact tools like radar sensors and audio analysis to monitor sleep from home. These systems analyze key signals like breathing, heart rate, and body movements, providing clinical-grade insights without disrupting sleep.
In January 2026, Stanford researchers introduced SleepFM, an AI model trained on 585,000 hours of sleep data. It predicts over 100 health conditions, including Parkinson’s and dementia, based on a single night’s data. Other AI tools, like radar-based systems, offer over 90% accuracy in detecting disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. These advancements mean earlier detection, personalized care, and better sleep health for everyone.
Mayo Clinic taps AI to help narrow the gender gap in diagnosing sleep apnea | Talking Points
How Non-Contact Sleep Disorder Detection Works
How AI-Powered Non-Contact Sleep Monitoring Works: From Sensor to Diagnosis
What Are Non-Contact Sleep Monitoring Technologies?
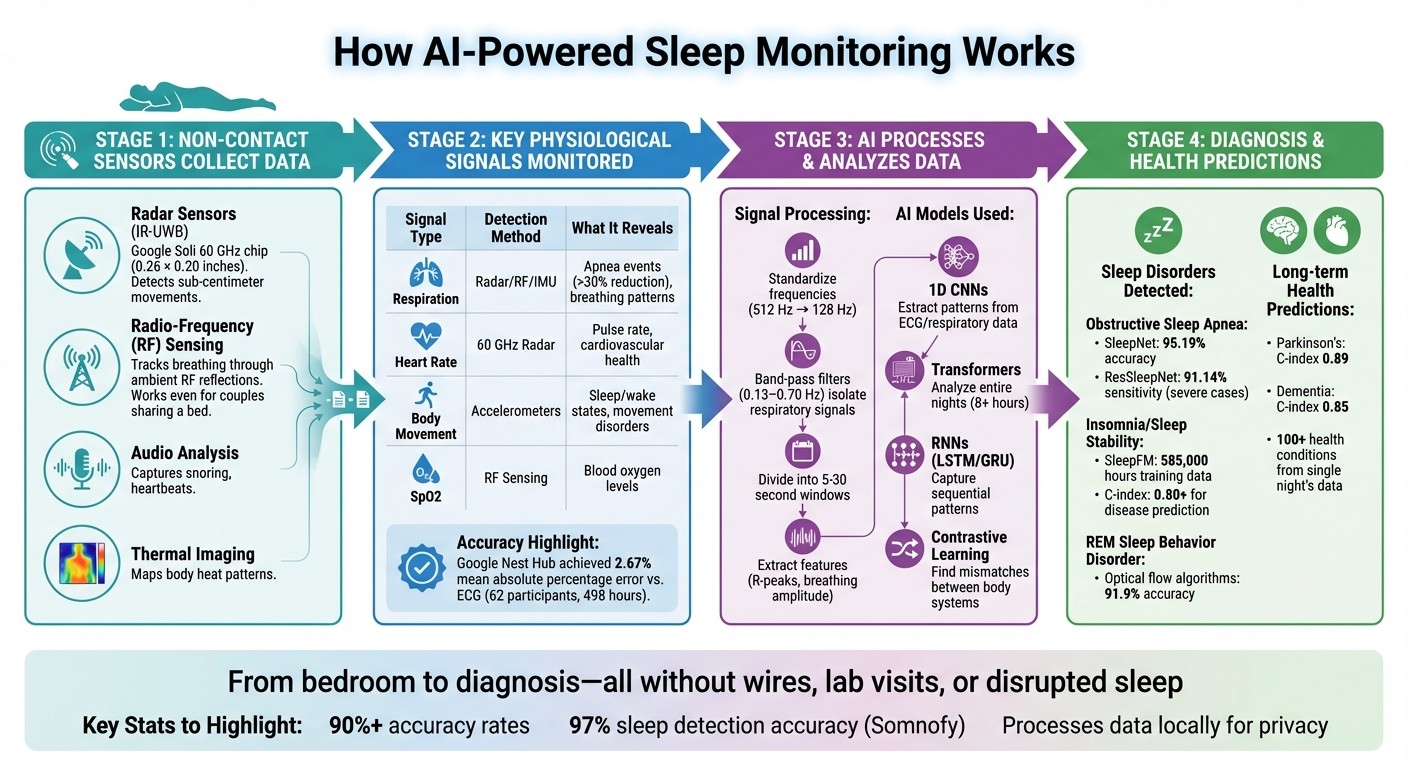
Non-contact sleep monitoring eliminates the need for wires, attachments, or clinical visits. These systems use radar sensors, radio-frequency (RF) sensing, audio analysis, and thermal imaging to track sleep patterns remotely. For example, IR-UWB radar can detect even the smallest movements, like the rise and fall of the chest during breathing [6][9]. Audio sensors pick up sounds such as snoring or heartbeats, while thermal cameras map body heat and monitor changes in physiology throughout the night [8]. Together, these tools form the backbone of precise, AI-powered sleep monitoring.
Take Google’s "Soli" technology as an example. In 2021, Google introduced its 60 GHz radar chip - tiny at just 0.26 by 0.20 inches - into the second-generation Nest Hub. This bedside device uses low-energy radar to track sub-centimeter body movements, all without relying on cameras or microphones. In a study involving 62 participants over 498 hours, it measured heart rate fluctuations with an impressive mean absolute percentage error of just 2.67% compared to traditional ECG methods [6][10]. Another standout is VitalThings’ Somnofy sleep assistant, which uses IR-UWB radar and machine learning. Validation studies showed it detected sleep accurately 97% of the time and aligned closely with polysomnography for identifying sleep stages [9].
Key Signals Monitored by AI
Using these technologies, AI focuses on critical physiological signals to evaluate sleep health. Respiration rate and amplitude are key indicators - AI systems can detect reductions of over 30% or complete pauses in breathing, flagging potential apnea events [11]. Heart rate is monitored through micro-movements caused by blood flow, even through layers of clothing or blankets [10]. Body movements help differentiate between sleep and wake states and can also identify disorders like restless limb movements [6][12]. Advanced RF systems can even estimate blood oxygen levels (SpO2) and other markers, such as C-reactive protein, without any direct skin contact [7].
Signal Type | Detection Method | What It Reveals |
|---|---|---|
Respiration | Radar/RF/IMU | Apnea events, breathing patterns |
Heart Rate | 60 GHz Radar | Pulse rate, cardiovascular health |
Body Movement | Accelerometers | Sleep/wake states, movement issues |
SpO2 | RF Sensing | Blood oxygen levels |
AI systems use advanced techniques like deep learning and signal processing to interpret these inputs. For instance, band-pass filters (0.13–0.70 Hz) isolate respiratory signals, while neural networks classify sleep stages - Wake, Light, Deep, and REM - and detect arousals [4][5][11]. In May 2025, MIT researcher Hao He developed a groundbreaking system that reads high-fidelity breathing signals from ambient RF reflections. Remarkably, it works even for couples sharing a bed, converting these signals into EEG-like sleep stage data [7].
Privacy is a key consideration in these systems. Most devices process raw sensor data locally, ensuring that only high-level summaries - such as "asleep" or "awake" - are uploaded [6].
The Role of AI Algorithms in Sleep Disorder Detection
AI Models and Techniques in Use
AI systems are revolutionizing sleep disorder detection by leveraging cutting-edge deep learning models to analyze physiological signals. For example, 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are adept at automatically extracting key features from data sources like ECG readings and respiratory rhythms, uncovering patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
More advanced approaches now incorporate transformer architectures, which allow for the analysis of entire nights of sleep instead of focusing on short, isolated segments. A great example of this is SleepFM, a model that demonstrates how AI can decode complex sleep behaviors across a wide range of individuals.
Another fascinating technique, contrastive learning, takes this a step further by exploring relationships between different data streams. It works by hiding one signal - like breathing patterns - and challenging the model to reconstruct it using other physiological inputs. This method reveals how various body systems interact during sleep. As Dr. Emmanuel Mignot, a sleep medicine professor at Stanford, puts it:
"The most information we got for predicting disease was by contrasting the different channels. Body constituents that were out of sync - a brain that looks asleep but a heart that looks awake, for example - seemed to spell trouble" [1].
In addition, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) - specifically Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) - excel at capturing sequential patterns and transitions throughout the night. On the other hand, optical flow algorithms, applied to infrared video footage, can detect subtle movements during REM sleep with impressive accuracy, reaching as high as 91.9% when identifying abnormal movements [14].
These sophisticated modeling techniques feed into a broader data processing system, ensuring that raw sensor inputs are transformed into actionable insights. This makes advanced sleep disorder detection not only highly effective but also more accessible for everyday users.
Processing and Analyzing Sleep Data
Once the AI models are in place, the system begins by rigorously preprocessing raw sensor data to ensure precise results. Signals captured at varying rates - for instance, 512 Hz for heart rate versus 1 Hz for oxygen levels - are standardized to a consistent frequency, often 128 Hz. These signals are then divided into short windows of 5 to 30 seconds for detailed analysis.
To filter out background noise, band-pass filters are employed, isolating critical signals like breathing patterns. From there, key features such as heartbeat R-peaks and changes in breathing amplitude are extracted, condensing the data into a format that's easier to classify.
This streamlined process transforms raw sensor readings into structured, meaningful data. The result? AI systems can detect events like sleep apnea and even predict long-term health risks. For instance, they’ve reported C-index values of 0.85 for dementia and 0.89 for Parkinson’s disease [1]. By automating these intricate tasks, AI-powered tools deliver clinical-grade insights without requiring uncomfortable overnight lab visits - making sleep health monitoring more accessible and user-friendly than ever.
Detecting Common Sleep Disorders with AI
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
AI has become a game-changer in identifying obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition that disrupts breathing during sleep. By analyzing breathing patterns and chest movements, AI systems can pinpoint interruptions with remarkable precision. OSA affects about 1 billion people worldwide, including 14% of men and 5% of women in the United States [16].
In July 2025, researchers introduced SleepNet, a system that integrates data from single-lead ECG, nasal airflow, and abdominal respiratory signals. Using a combination of 1D-CNN and Bi-GRU models to examine 60-second data segments, SleepNet achieved a 95.19% diagnostic accuracy, with a sensitivity of 96.12% and specificity of 93.45% [16]. This multi-data approach outperformed older methods that relied on a single data source.
AI has also advanced in non-contact diagnostics. Early in 2025, researchers developed ResSleepNet, a millimeter-wave radar-based framework that tracks chest and abdomen movements without requiring physical contact. After training on 15,785 nights of data and testing on 221 nights, the system achieved an Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) of 0.87 for Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) estimation and a sensitivity of 91.14% for detecting severe sleep-disordered breathing [2]. This radar-based method eliminates the discomfort of wearable devices while maintaining clinical-grade accuracy.
"Radar-based non-contact sensing offers a promising solution. These systems accurately capture thoracoabdominal movement signals during sleep without requiring physical contact, thereby eliminating the discomfort and compliance issues associated with wearable devices and PSG" [2].
Beyond detecting apnea, AI is now uncovering subtler signs of disrupted sleep that can impact overall quality.
Insomnia and Sleep Stability Issues
AI technology is also tackling sleep disorders like insomnia and stability problems that don’t involve obstructive events. By analyzing physiological signals, AI can detect when the brain appears to be asleep, but the heart rate or other metrics suggest otherwise - uncovering issues that traditional methods often miss.
In January 2026, Stanford Medicine researchers, led by Emmanuel Mignot and James Zou, introduced SleepFM, a foundation model trained on 585,000 hours of sleep data from 65,000 participants. Using contrastive learning, SleepFM reconstructs missing physiological signals and identifies mismatched patterns. This model detects when body systems are out of sync during sleep, predicting disease risk with a C-index of 0.80 or higher [1][15].
Another breakthrough came in March 2025 when the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai developed PFTSleep, a transformer-based model analyzing over 1 million hours of sleep data. Led by Benjamin Fox and Dr. Ankit Parekh, this system evaluates brain waves, muscle activity, heart rate, and breathing patterns across entire nights. Unlike shorter analyses, this comprehensive approach reveals subtle sleep stability issues [13].
AI tools also focus on metrics like micro-arousals, sleep onset latency, and frequent transitions between deep and lighter sleep stages. Insights like these are critical, especially since 62% of people globally report dissatisfaction with their sleep quality, often due to undiagnosed stability problems [18].
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder and Other Conditions
AI has also proven effective in diagnosing REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) and related conditions. By analyzing muscle movements and activity patterns during REM sleep, AI-powered optical flow algorithms applied to infrared video can detect abnormal movements with an accuracy of 91.9% [14].
In June 2025, Vanderbilt University’s Assistant Professor Yayun Du introduced LMA-SleepNet, a machine learning framework paired with a skin-mounted sensor. This system analyzes 140 features, focusing on breathing patterns and muscle activity as key markers for REM sleep transitions and wake periods [17].
The technology tracks limb movements, body temperature, and respiratory effort to create a detailed picture of REM sleep behavior. By processing these data streams simultaneously, AI can identify the muscle twitches and movements that signal RBD - often years before serious neurological conditions appear. This early detection capability is crucial for long-term health monitoring and disease prevention.
Benefits of AI-Powered Sleep Detection for Everyday Use
Accuracy and Non-Intrusive Monitoring
AI-powered sleep detection has revolutionized how we monitor sleep by combining clinical-grade precision with convenience. Unlike traditional polysomnography (PSG), which requires multiple sensors and a lab environment, modern systems offer accuracy rates exceeding 90%, with some models reaching an impressive 99.09% in diagnosing eight different sleep disorders [20]. PSG setups, while effective, often disrupt natural sleep patterns due to the "first-night effect", where patients sleep differently in unfamiliar settings [19].
Contactless solutions, like ultra-low-power radiofrequency biomotion monitors, achieve over 90% accuracy in independent tests [22]. Similarly, smartphone-based sonar technology delivers accuracy rates above 85% compared to PSG [22]. Bedside radar systems, which track even the tiniest movements, boast 87% accuracy for distinguishing between sleep and wake states [6].
What sets AI apart is its ability to analyze entire nights of sleep - capturing over eight hours of continuous data - rather than relying on short, 30-second segments [13]. This comprehensive approach reveals patterns that manual analysis often misses and reduces inconsistencies between scorers [20][21]. Dr. Girish N. Nadkarni from Mount Sinai highlights this advantage:
"By analyzing entire nights of sleep with greater consistency, we can uncover deeper insights into sleep health and its connection to overall well-being" [13].
The combination of high accuracy and non-intrusive monitoring makes it easier than ever to track and improve sleep quality using health data. These advancements pave the way for personalized sleep solutions, offering actionable insights for better rest.
How Healify Improves Sleep Health
Healify transforms complex sleep data into practical, easy-to-follow recommendations. By analyzing data from wearables and other health sources, Healify evaluates over 83 sleep markers to provide a detailed picture of your sleep quality [22]. Instead of bombarding users with raw numbers, Healify's AI health coach, Anna, simplifies the information into personalized, science-backed suggestions.
Using its advanced detection capabilities, Healify identifies subtle sleep issues by analyzing patterns across multiple nights. For example, it can flag cases where your brain seems to be asleep, but your heart rate indicates otherwise [1]. Its foundational models can predict over 100 health conditions, enabling early identification and intervention for potential sleep-related problems.
Healify also offers real-time monitoring, instant health alerts, and tailored action plans, turning raw health data into clear, actionable steps. With these tools, users can take control of their sleep and overall wellness, making meaningful improvements night after night.
Conclusion: The Future of AI in Sleep Health
AI is reshaping how we detect and manage sleep disorders. Tasks that once required costly overnight lab studies and bulky, intrusive equipment are now transitioning to at-home solutions. Wearables and contactless sensors, like radar and sonar, are making sleep monitoring easier and more accessible [3][23]. This shift is paving the way for broader screening and earlier intervention.
But AI’s role doesn’t stop at detection - it’s also transforming how care is personalized. In January 2026, researchers at Stanford Medicine, led by Emmanuel Mignot and James Zou, introduced SleepFM, an AI foundation model capable of analyzing a single night’s sleep data to predict a wide range of health conditions. By leveraging extensive sleep datasets, SleepFM can forecast diseases such as Parkinson’s and heart attacks with remarkable accuracy [1]. This development represents a move from reactive diagnosis to proactive, predictive care - a logical next step in the evolution of AI-driven sleep health.
AI is also breaking new ground in predicting conditions like dementia, cancer, and heart disease years before symptoms surface [1]. As these technologies advance, they will refine treatment precision by identifying specific physiological markers, enabling more tailored and effective care [24].
Companies like Healify are already integrating these advancements into everyday tools. Healify’s AI health coach, Anna, takes complex sleep data from wearables and other physiological signals and translates it into actionable insights. This makes optimizing your sleep and overall well-being more straightforward and achievable.
The future of sleep health isn’t just about improving detection - it’s about seamlessly integrating clinical-grade monitoring into daily life. With AI, your sleep data can become a powerful tool for guiding long-term wellness.
FAQs
How does AI make sleep disorder detection more accurate than traditional methods?
AI is transforming the way sleep disorders are detected by analyzing multiple types of physiological data simultaneously - think heart rate variability, breathing patterns, and body movements. This approach helps uncover subtle signs of conditions like sleep apnea or narcolepsy that might slip through the cracks during traditional, manually scored sleep studies.
One major advantage? AI eliminates the inconsistencies that can arise from human scoring, where results might vary depending on the technician. Instead, it delivers consistent and reliable assessments. Plus, AI can process data collected over several nights from wearable devices or non-contact sensors, painting a fuller picture of someone’s sleep habits. By blending advanced algorithms with detailed, long-term data, AI enables earlier and more precise detection of potential sleep issues, making the process both more accurate and tailored to the individual.
How do AI-powered sleep monitoring systems protect my privacy?
AI-powered sleep monitoring systems are designed with robust security measures to keep your personal data safe. Using advanced encryption methods like AES-256, they protect your information during both transmission and storage. On top of that, these systems practice strict data-minimization, meaning they only collect and process the data that's absolutely necessary.
In the U.S., regulations such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) empower users to take control of their data. This includes options to view, delete, or opt out of specific data uses. Many platforms also anonymize data when training AI models and offer tools that let users manage permissions or revoke access whenever they choose.
These safeguards ensure that your sleep data is handled securely, allowing you to gain health insights without compromising your privacy.
Can AI use sleep data to predict future health risks?
Yes, AI-driven systems have the ability to analyze sleep patterns and uncover potential risks linked to over 100 long-term health conditions. By evaluating aspects like how long you sleep, the quality of your rest, and any interruptions, these systems deliver meaningful insights into your overall health and possible future issues.
This cutting-edge technology processes enormous amounts of data to spot early indicators of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and mental health challenges. It offers a forward-thinking way to address health concerns and enhance well-being.
Related Blog Posts
AI is transforming sleep health by offering faster, more accessible ways to detect sleep disorders. Traditionally, diagnosing conditions like sleep apnea or insomnia required overnight lab tests with complex equipment, which are expensive and inconvenient. Now, AI-driven systems use non-contact tools like radar sensors and audio analysis to monitor sleep from home. These systems analyze key signals like breathing, heart rate, and body movements, providing clinical-grade insights without disrupting sleep.
In January 2026, Stanford researchers introduced SleepFM, an AI model trained on 585,000 hours of sleep data. It predicts over 100 health conditions, including Parkinson’s and dementia, based on a single night’s data. Other AI tools, like radar-based systems, offer over 90% accuracy in detecting disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. These advancements mean earlier detection, personalized care, and better sleep health for everyone.
Mayo Clinic taps AI to help narrow the gender gap in diagnosing sleep apnea | Talking Points

How Non-Contact Sleep Disorder Detection Works

How AI-Powered Non-Contact Sleep Monitoring Works: From Sensor to Diagnosis
What Are Non-Contact Sleep Monitoring Technologies?
Non-contact sleep monitoring eliminates the need for wires, attachments, or clinical visits. These systems use radar sensors, radio-frequency (RF) sensing, audio analysis, and thermal imaging to track sleep patterns remotely. For example, IR-UWB radar can detect even the smallest movements, like the rise and fall of the chest during breathing [6][9]. Audio sensors pick up sounds such as snoring or heartbeats, while thermal cameras map body heat and monitor changes in physiology throughout the night [8]. Together, these tools form the backbone of precise, AI-powered sleep monitoring.
Take Google’s "Soli" technology as an example. In 2021, Google introduced its 60 GHz radar chip - tiny at just 0.26 by 0.20 inches - into the second-generation Nest Hub. This bedside device uses low-energy radar to track sub-centimeter body movements, all without relying on cameras or microphones. In a study involving 62 participants over 498 hours, it measured heart rate fluctuations with an impressive mean absolute percentage error of just 2.67% compared to traditional ECG methods [6][10]. Another standout is VitalThings’ Somnofy sleep assistant, which uses IR-UWB radar and machine learning. Validation studies showed it detected sleep accurately 97% of the time and aligned closely with polysomnography for identifying sleep stages [9].
Key Signals Monitored by AI
Using these technologies, AI focuses on critical physiological signals to evaluate sleep health. Respiration rate and amplitude are key indicators - AI systems can detect reductions of over 30% or complete pauses in breathing, flagging potential apnea events [11]. Heart rate is monitored through micro-movements caused by blood flow, even through layers of clothing or blankets [10]. Body movements help differentiate between sleep and wake states and can also identify disorders like restless limb movements [6][12]. Advanced RF systems can even estimate blood oxygen levels (SpO2) and other markers, such as C-reactive protein, without any direct skin contact [7].
Signal Type | Detection Method | What It Reveals |
|---|---|---|
Respiration | Radar/RF/IMU | Apnea events, breathing patterns |
Heart Rate | 60 GHz Radar | Pulse rate, cardiovascular health |
Body Movement | Accelerometers | Sleep/wake states, movement issues |
SpO2 | RF Sensing | Blood oxygen levels |
AI systems use advanced techniques like deep learning and signal processing to interpret these inputs. For instance, band-pass filters (0.13–0.70 Hz) isolate respiratory signals, while neural networks classify sleep stages - Wake, Light, Deep, and REM - and detect arousals [4][5][11]. In May 2025, MIT researcher Hao He developed a groundbreaking system that reads high-fidelity breathing signals from ambient RF reflections. Remarkably, it works even for couples sharing a bed, converting these signals into EEG-like sleep stage data [7].
Privacy is a key consideration in these systems. Most devices process raw sensor data locally, ensuring that only high-level summaries - such as "asleep" or "awake" - are uploaded [6].
The Role of AI Algorithms in Sleep Disorder Detection
AI Models and Techniques in Use
AI systems are revolutionizing sleep disorder detection by leveraging cutting-edge deep learning models to analyze physiological signals. For example, 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are adept at automatically extracting key features from data sources like ECG readings and respiratory rhythms, uncovering patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
More advanced approaches now incorporate transformer architectures, which allow for the analysis of entire nights of sleep instead of focusing on short, isolated segments. A great example of this is SleepFM, a model that demonstrates how AI can decode complex sleep behaviors across a wide range of individuals.
Another fascinating technique, contrastive learning, takes this a step further by exploring relationships between different data streams. It works by hiding one signal - like breathing patterns - and challenging the model to reconstruct it using other physiological inputs. This method reveals how various body systems interact during sleep. As Dr. Emmanuel Mignot, a sleep medicine professor at Stanford, puts it:
"The most information we got for predicting disease was by contrasting the different channels. Body constituents that were out of sync - a brain that looks asleep but a heart that looks awake, for example - seemed to spell trouble" [1].
In addition, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) - specifically Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) - excel at capturing sequential patterns and transitions throughout the night. On the other hand, optical flow algorithms, applied to infrared video footage, can detect subtle movements during REM sleep with impressive accuracy, reaching as high as 91.9% when identifying abnormal movements [14].
These sophisticated modeling techniques feed into a broader data processing system, ensuring that raw sensor inputs are transformed into actionable insights. This makes advanced sleep disorder detection not only highly effective but also more accessible for everyday users.
Processing and Analyzing Sleep Data
Once the AI models are in place, the system begins by rigorously preprocessing raw sensor data to ensure precise results. Signals captured at varying rates - for instance, 512 Hz for heart rate versus 1 Hz for oxygen levels - are standardized to a consistent frequency, often 128 Hz. These signals are then divided into short windows of 5 to 30 seconds for detailed analysis.
To filter out background noise, band-pass filters are employed, isolating critical signals like breathing patterns. From there, key features such as heartbeat R-peaks and changes in breathing amplitude are extracted, condensing the data into a format that's easier to classify.
This streamlined process transforms raw sensor readings into structured, meaningful data. The result? AI systems can detect events like sleep apnea and even predict long-term health risks. For instance, they’ve reported C-index values of 0.85 for dementia and 0.89 for Parkinson’s disease [1]. By automating these intricate tasks, AI-powered tools deliver clinical-grade insights without requiring uncomfortable overnight lab visits - making sleep health monitoring more accessible and user-friendly than ever.
Detecting Common Sleep Disorders with AI
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
AI has become a game-changer in identifying obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition that disrupts breathing during sleep. By analyzing breathing patterns and chest movements, AI systems can pinpoint interruptions with remarkable precision. OSA affects about 1 billion people worldwide, including 14% of men and 5% of women in the United States [16].
In July 2025, researchers introduced SleepNet, a system that integrates data from single-lead ECG, nasal airflow, and abdominal respiratory signals. Using a combination of 1D-CNN and Bi-GRU models to examine 60-second data segments, SleepNet achieved a 95.19% diagnostic accuracy, with a sensitivity of 96.12% and specificity of 93.45% [16]. This multi-data approach outperformed older methods that relied on a single data source.
AI has also advanced in non-contact diagnostics. Early in 2025, researchers developed ResSleepNet, a millimeter-wave radar-based framework that tracks chest and abdomen movements without requiring physical contact. After training on 15,785 nights of data and testing on 221 nights, the system achieved an Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) of 0.87 for Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) estimation and a sensitivity of 91.14% for detecting severe sleep-disordered breathing [2]. This radar-based method eliminates the discomfort of wearable devices while maintaining clinical-grade accuracy.
"Radar-based non-contact sensing offers a promising solution. These systems accurately capture thoracoabdominal movement signals during sleep without requiring physical contact, thereby eliminating the discomfort and compliance issues associated with wearable devices and PSG" [2].
Beyond detecting apnea, AI is now uncovering subtler signs of disrupted sleep that can impact overall quality.
Insomnia and Sleep Stability Issues
AI technology is also tackling sleep disorders like insomnia and stability problems that don’t involve obstructive events. By analyzing physiological signals, AI can detect when the brain appears to be asleep, but the heart rate or other metrics suggest otherwise - uncovering issues that traditional methods often miss.
In January 2026, Stanford Medicine researchers, led by Emmanuel Mignot and James Zou, introduced SleepFM, a foundation model trained on 585,000 hours of sleep data from 65,000 participants. Using contrastive learning, SleepFM reconstructs missing physiological signals and identifies mismatched patterns. This model detects when body systems are out of sync during sleep, predicting disease risk with a C-index of 0.80 or higher [1][15].
Another breakthrough came in March 2025 when the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai developed PFTSleep, a transformer-based model analyzing over 1 million hours of sleep data. Led by Benjamin Fox and Dr. Ankit Parekh, this system evaluates brain waves, muscle activity, heart rate, and breathing patterns across entire nights. Unlike shorter analyses, this comprehensive approach reveals subtle sleep stability issues [13].
AI tools also focus on metrics like micro-arousals, sleep onset latency, and frequent transitions between deep and lighter sleep stages. Insights like these are critical, especially since 62% of people globally report dissatisfaction with their sleep quality, often due to undiagnosed stability problems [18].
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder and Other Conditions
AI has also proven effective in diagnosing REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) and related conditions. By analyzing muscle movements and activity patterns during REM sleep, AI-powered optical flow algorithms applied to infrared video can detect abnormal movements with an accuracy of 91.9% [14].
In June 2025, Vanderbilt University’s Assistant Professor Yayun Du introduced LMA-SleepNet, a machine learning framework paired with a skin-mounted sensor. This system analyzes 140 features, focusing on breathing patterns and muscle activity as key markers for REM sleep transitions and wake periods [17].
The technology tracks limb movements, body temperature, and respiratory effort to create a detailed picture of REM sleep behavior. By processing these data streams simultaneously, AI can identify the muscle twitches and movements that signal RBD - often years before serious neurological conditions appear. This early detection capability is crucial for long-term health monitoring and disease prevention.
Benefits of AI-Powered Sleep Detection for Everyday Use
Accuracy and Non-Intrusive Monitoring
AI-powered sleep detection has revolutionized how we monitor sleep by combining clinical-grade precision with convenience. Unlike traditional polysomnography (PSG), which requires multiple sensors and a lab environment, modern systems offer accuracy rates exceeding 90%, with some models reaching an impressive 99.09% in diagnosing eight different sleep disorders [20]. PSG setups, while effective, often disrupt natural sleep patterns due to the "first-night effect", where patients sleep differently in unfamiliar settings [19].
Contactless solutions, like ultra-low-power radiofrequency biomotion monitors, achieve over 90% accuracy in independent tests [22]. Similarly, smartphone-based sonar technology delivers accuracy rates above 85% compared to PSG [22]. Bedside radar systems, which track even the tiniest movements, boast 87% accuracy for distinguishing between sleep and wake states [6].
What sets AI apart is its ability to analyze entire nights of sleep - capturing over eight hours of continuous data - rather than relying on short, 30-second segments [13]. This comprehensive approach reveals patterns that manual analysis often misses and reduces inconsistencies between scorers [20][21]. Dr. Girish N. Nadkarni from Mount Sinai highlights this advantage:
"By analyzing entire nights of sleep with greater consistency, we can uncover deeper insights into sleep health and its connection to overall well-being" [13].
The combination of high accuracy and non-intrusive monitoring makes it easier than ever to track and improve sleep quality using health data. These advancements pave the way for personalized sleep solutions, offering actionable insights for better rest.
How Healify Improves Sleep Health

Healify transforms complex sleep data into practical, easy-to-follow recommendations. By analyzing data from wearables and other health sources, Healify evaluates over 83 sleep markers to provide a detailed picture of your sleep quality [22]. Instead of bombarding users with raw numbers, Healify's AI health coach, Anna, simplifies the information into personalized, science-backed suggestions.
Using its advanced detection capabilities, Healify identifies subtle sleep issues by analyzing patterns across multiple nights. For example, it can flag cases where your brain seems to be asleep, but your heart rate indicates otherwise [1]. Its foundational models can predict over 100 health conditions, enabling early identification and intervention for potential sleep-related problems.
Healify also offers real-time monitoring, instant health alerts, and tailored action plans, turning raw health data into clear, actionable steps. With these tools, users can take control of their sleep and overall wellness, making meaningful improvements night after night.
Conclusion: The Future of AI in Sleep Health
AI is reshaping how we detect and manage sleep disorders. Tasks that once required costly overnight lab studies and bulky, intrusive equipment are now transitioning to at-home solutions. Wearables and contactless sensors, like radar and sonar, are making sleep monitoring easier and more accessible [3][23]. This shift is paving the way for broader screening and earlier intervention.
But AI’s role doesn’t stop at detection - it’s also transforming how care is personalized. In January 2026, researchers at Stanford Medicine, led by Emmanuel Mignot and James Zou, introduced SleepFM, an AI foundation model capable of analyzing a single night’s sleep data to predict a wide range of health conditions. By leveraging extensive sleep datasets, SleepFM can forecast diseases such as Parkinson’s and heart attacks with remarkable accuracy [1]. This development represents a move from reactive diagnosis to proactive, predictive care - a logical next step in the evolution of AI-driven sleep health.
AI is also breaking new ground in predicting conditions like dementia, cancer, and heart disease years before symptoms surface [1]. As these technologies advance, they will refine treatment precision by identifying specific physiological markers, enabling more tailored and effective care [24].
Companies like Healify are already integrating these advancements into everyday tools. Healify’s AI health coach, Anna, takes complex sleep data from wearables and other physiological signals and translates it into actionable insights. This makes optimizing your sleep and overall well-being more straightforward and achievable.
The future of sleep health isn’t just about improving detection - it’s about seamlessly integrating clinical-grade monitoring into daily life. With AI, your sleep data can become a powerful tool for guiding long-term wellness.
FAQs
How does AI make sleep disorder detection more accurate than traditional methods?
AI is transforming the way sleep disorders are detected by analyzing multiple types of physiological data simultaneously - think heart rate variability, breathing patterns, and body movements. This approach helps uncover subtle signs of conditions like sleep apnea or narcolepsy that might slip through the cracks during traditional, manually scored sleep studies.
One major advantage? AI eliminates the inconsistencies that can arise from human scoring, where results might vary depending on the technician. Instead, it delivers consistent and reliable assessments. Plus, AI can process data collected over several nights from wearable devices or non-contact sensors, painting a fuller picture of someone’s sleep habits. By blending advanced algorithms with detailed, long-term data, AI enables earlier and more precise detection of potential sleep issues, making the process both more accurate and tailored to the individual.
How do AI-powered sleep monitoring systems protect my privacy?
AI-powered sleep monitoring systems are designed with robust security measures to keep your personal data safe. Using advanced encryption methods like AES-256, they protect your information during both transmission and storage. On top of that, these systems practice strict data-minimization, meaning they only collect and process the data that's absolutely necessary.
In the U.S., regulations such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) empower users to take control of their data. This includes options to view, delete, or opt out of specific data uses. Many platforms also anonymize data when training AI models and offer tools that let users manage permissions or revoke access whenever they choose.
These safeguards ensure that your sleep data is handled securely, allowing you to gain health insights without compromising your privacy.
Can AI use sleep data to predict future health risks?
Yes, AI-driven systems have the ability to analyze sleep patterns and uncover potential risks linked to over 100 long-term health conditions. By evaluating aspects like how long you sleep, the quality of your rest, and any interruptions, these systems deliver meaningful insights into your overall health and possible future issues.
This cutting-edge technology processes enormous amounts of data to spot early indicators of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and mental health challenges. It offers a forward-thinking way to address health concerns and enhance well-being.
Related Blog Posts
Endlich die Kontrolle über Ihre Gesundheit übernehmen

Endlich die Kontrolle über Ihre Gesundheit übernehmen

Endlich die Kontrolle über Ihre Gesundheit übernehmen



