Improve your health
Improve your health
Improve your health
10 de enero de 2026
Ultimate Guide to AI Allergen Detection


Food allergies affect millions of Americans, with 8% of children and 10% of adults at risk of severe reactions. A single mistake in identifying allergens can lead to life-threatening situations, and undeclared allergens are a major issue for both consumers and food manufacturers. Traditional detection methods like ELISA and PCR are often slow, destructive, and require specialized expertise, leaving room for improvement.
AI-powered allergen detection is changing the game by offering faster, more precise, and non-destructive solutions. Using advanced sensors like hyperspectral imaging and FTIR spectroscopy combined with machine learning, these tools can identify allergens with high accuracy. They’re already being used in manufacturing, restaurants, and even personal devices to improve safety and compliance with FDA regulations.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
How AI is transforming allergen detection with technologies like biosensors and electronic noses.
The role of machine learning models in identifying and quantifying allergens.
How AI tools are improving food safety in manufacturing, restaurants, and personal allergy management.
Key challenges, such as regulatory compliance, data quality, and ethical considerations.
AI allergen detection is reshaping food safety, offering practical solutions for manufacturers and safer choices for consumers.
This Device Can Detect Allergens in Food | Innovation Nation
Technologies That Power AI Allergen Detection
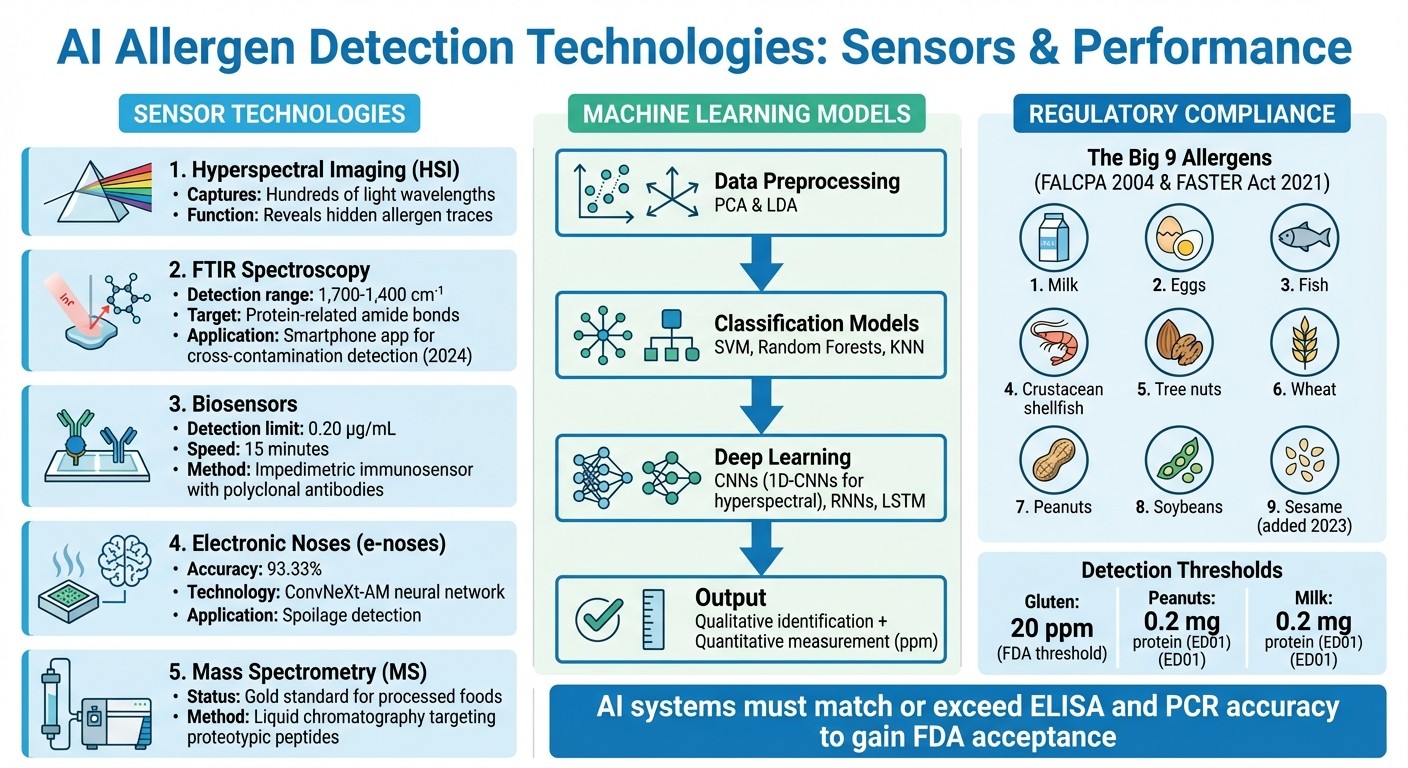
AI Allergen Detection Technologies: Sensors, Accuracy Rates, and Detection Capabilities
AI allergen detection combines advanced sensors, machine learning, and regulatory compliance to deliver quicker, more precise results in food safety.
Sensors and Data Collection Methods
Modern AI systems rely on non-invasive sensors that analyze food without damaging the sample, allowing manufacturers to test products while keeping them market-ready.
Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI): This technique merges photography and spectroscopy to capture hundreds of light wavelengths, revealing hidden allergen traces in food [5].
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy: FTIR uses infrared light to identify molecular bonds in food. By focusing on the 1,700–1,400 cm⁻¹ range, it detects protein-related amide bonds where allergens often reside. In March 2024, researchers Adedeji, Okeke, and Rady developed a smartphone app that uses FTIR data to identify cross-contamination in corn flour [1].
Biosensors: These devices combine biological components, like antibodies, with electronic transducers. A study in June 2023 introduced an impedimetric immunosensor capable of detecting chicken egg ovalbumin at 0.20 µg/mL in just 15 minutes. The system used polyclonal antibodies attached to a gold surface to monitor allergen traces without harming the sample [4].
Electronic Noses (e-noses): These devices use gas sensor arrays to identify volatile organic compounds in food. In early 2026, a study published in Food Control demonstrated that an e-nose paired with a ConvNeXt-AM neural network achieved 93.33% accuracy in detecting spoilage in Hami melons [5].
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Known as the gold standard for processed foods, MS uses liquid chromatography to target proteotypic peptides, offering unmatched sensitivity [6].
These sensors collect precise data, which machine learning models then analyze to generate actionable insights.
Machine Learning Models for Allergen Identification
Once sensor data is collected, machine learning models process and interpret it, identifying allergens with remarkable accuracy. Raw data from sensors is complex, so preprocessing techniques like PCA (Principal Component Analysis) and LDA (Linear Discriminant Analysis) are used to simplify the data and highlight key allergen signals [5].
Classification Models: Algorithms such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests (RF), and k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) are trained on labeled data to identify allergens in new samples [5].
Deep Learning Models: For more complex food compositions, deep learning is increasingly preferred. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), especially 1D-CNNs, excel at analyzing hyperspectral data, detecting allergens across surfaces or within mixtures. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models are ideal for sequential data, such as that from electronic noses, as they track changes over time [5].
These models provide both qualitative insights (identifying which allergen is present) and quantitative measurements (determining the amount, often in parts per million). This capability supports both quality control and adherence to regulatory standards.
Meeting FDA and U.S. Regulatory Requirements
AI allergen detection systems must align with strict U.S. food safety regulations to ensure compliance and consumer safety.
The Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act (FALCPA) of 2004 and the FASTER Act of 2021 require clear labeling of the "Big 9" allergens: milk, eggs, fish, Crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, wheat, peanuts, soybeans, and sesame. Additionally, 21 CFR Part 117 mandates food facilities to implement preventive controls to minimize allergen cross-contact [7][8][9].
While the FDA has set a gluten threshold of 20 ppm for "gluten-free" claims, no general thresholds exist for other allergens. AI systems must be validated to detect even trace amounts that could trigger allergic reactions [9][1]. Traditional methods like ELISA and PCR remain the FDA's primary enforcement tools, so AI technologies need to demonstrate comparable or better accuracy to gain acceptance [9].
"Finding problems before they can potentially harm consumers is a critical element of the FDA's allergen enforcement program." - U.S. Food and Drug Administration [1]
Facilities adopting AI detection technologies must ensure their food safety plans comply with 21 CFR 117.170, which requires reanalysis whenever new hazard information arises [11]. Employee training on allergen cross-contact prevention is also mandatory, regardless of the detection tools in use [10].
Where AI Allergen Detection is Used
With advancements in detection methods, AI is now being used to monitor allergen risks in real time. From factory floors to restaurant kitchens and even personal devices, these systems are transforming how allergen-related challenges are identified and addressed.
Food Manufacturing and Supply Chain Monitoring
Food manufacturers face considerable financial and legal risks from allergen contamination, with recalls potentially costing up to 15% of their annual revenue [1].
AI has stepped in to help. On production lines, tools like computer vision and FTIR spectroscopy monitor operations in real time, while predictive analytics use environmental and historical data to flag potential risks [1][13].
In a significant development, the FDA entered the third phase of its Artificial Intelligence Imported Seafood Pilot program in March 2024. This initiative uses AI and machine learning to enhance the screening of imports at U.S. ports [12]. The FDA has also partnered with industry leaders to establish the Leafy Greens Data Trust, a shared database designed to predict and prevent outbreaks in one of the most contamination-prone food categories [13].
Blockchain and AI-powered traceability systems are replacing outdated paper records. These digital tools can track contaminated food within seconds, allowing manufacturers to quickly address safety concerns [13].
"Smarter food safety is about more than just technology. It's also about simpler, more effective, and modern approaches and processes." - FDA Blueprint [13]
These advancements extend from the manufacturing floor to the dining table, ensuring better safety throughout the supply chain.
Restaurant and Hospitality Applications
Managing allergens in restaurants is no small task. Around 9% of Americans - about 33 million people - live with food allergies [14][15], and cases of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) increased by 377% between 2007 and 2016 [15].
In 2024, Papa Johns teamed up with LiberEat to introduce AI allergen detection technology, offering an extra layer of safety against allergen risks [18].
AI-powered digital menus now allow diners to filter dishes based on specific allergies, reducing the chances of human error and lightening the load on staff. These systems also connect with Point-of-Sale (POS) terminals to flag potential allergen risks during dish customizations, ensuring safer food preparation [16].
At CES 2026, Allergen Alert unveiled a portable "mini lab" created with bioMérieux. This device uses automated immunoassay technology to test for allergens on-site, delivering results in minutes. At a cost of $200, with single-use testing pouches priced under $10 or available via subscription, this tool offers a practical solution for quick allergen detection [14][17].
These innovations are not just limited to restaurants - they complement tools designed for personal allergen management.
Personal Allergy Management Tools
For individuals with food allergies, AI-powered apps and devices are becoming game changers. These tools help users scan food labels, analyze meals, and track allergic reactions in real time.
Handheld devices equipped with AI sensors, such as FTIR and hyperspectral imaging, can detect allergenic proteins without harming the food. This allows users to test their meals on the spot, providing an extra layer of safety [1].
Apps like Healify take allergen management a step further by integrating it into overall health monitoring. Healify’s AI health coach, Anna, uses data from wearables, biometrics, and lifestyle inputs to identify patterns between food intake and allergic reactions, offering tailored advice to help users avoid triggers.
Meanwhile, AI-powered meal-photo counters are achieving accuracy rates between 62% and 99% [19], making allergen management tools more accessible and reliable for millions of people in the U.S. and beyond.
Data Quality, Safety, and Ethics in AI Allergen Detection
AI allergen detection systems are expected to provide fast and precise results while also safeguarding sensitive data. This is particularly important given that one-third of serious food safety risks reported by the FDA involve undeclared allergens [1][9]. Achieving this balance requires handling large datasets responsibly while respecting individual privacy.
Accuracy and Validation Requirements
The reliability of AI-based allergen detection systems depends heavily on the quality of the data used for training. To ensure dependable results, these systems are validated against established gold standards like ELISA, PCR, and Mass Spectrometry [1][9]. For instance, the FDA employs its xMAP assay, which can detect up to 16 allergens in a single test, to oversee food safety and verify labeling accuracy [9].
Key performance metrics for these systems include sensitivity (accurately identifying allergens) and specificity (minimizing false positives) [1]. These tools must be capable of detecting trace amounts of allergens, such as 0.2 mg of protein for peanuts and milk - their respective ED01 thresholds [1].
"Sensor and machine learning coupling in allergen detection is a classic example of artificial intelligence (AI) deployment within the food supply chain with the capability to increase the sustainability of the allergen detection method and reduce the human involvement and response time for reliable feedback." - Akinbode A Adedeji et al. [1]
Manufacturers are encouraged to use multi-method validation to cross-check AI results, such as using two different ELISA kits or combining ELISA with DNA-based PCR methods [9]. Additionally, under 21 CFR part 117, food facilities must implement preventive controls and accurate labeling practices to ensure allergens are properly disclosed [8].
Technical validation creates a foundation for addressing broader concerns like privacy and ethics. By ensuring detection systems are both safe and reliable, manufacturers can foster consumer confidence in AI-driven health solutions.
Privacy and Ethical Design in AI Systems
Beyond achieving technical accuracy, ethical considerations play a crucial role in the design of AI allergen detection systems. These tools, particularly personal health apps, often collect sensitive information about users' diets and medical histories. This creates a challenge: how to build comprehensive datasets without compromising individual privacy [20].
In the U.S., AI systems must adhere to regulations such as the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) and meet manufacturing standards outlined in 21 CFR part 117 [8][9]. Privacy-conscious tools must also secure informed consent and address algorithmic bias [20].
"The price of innovation does not need to be the erosion of fundamental privacy rights." - Elizabeth Denham, Information Commissioner [20]
Transparency is another critical factor. Many AI models function as "black boxes", making it difficult to understand how decisions are made [20]. Developers should adopt principles like "accountability-by-design" and "transparency-by-design" to ensure their systems are interpretable. Tools like SHAP can help make AI decision-making processes clearer for users [21]. Additionally, third-party or government audits can strike a balance between protecting intellectual property and ensuring algorithmic transparency [20].
Algorithmic bias is another pressing issue. To ensure fairness and reliability, training datasets must be diverse. Models built on homogeneous data may fail to perform well for underrepresented groups [21]. For example, systems trained primarily on European populations might yield inaccurate results for Asian or African users, whose allergen sensitization patterns differ [21]. Addressing these gaps is essential for creating equitable and trustworthy AI solutions.
The Future of AI Allergen Detection
AI is reshaping how allergens are detected, shifting the process from reactive to proactive and even personalized. The food industry is embracing cutting-edge digital tools that combine sensors with machine learning to boost both the speed and safety of allergen detection [1]. Technologies like hyperspectral imaging and near-infrared spectroscopy allow manufacturers to pinpoint trace allergens without harming food samples. This makes real-time quality control not only practical but also more cost-efficient [1]. These advancements streamline production and open the door to innovations in personal allergen management.
For consumers, this evolution is just as impactful. Wearable biosensors and smartphone-integrated tools are on the horizon, offering real-time alerts for allergic reactions and enabling quick meal testing [1][2][21]. Imagine snapping a photo of your meal and having computer vision identify ingredients with about 90% accuracy [22]. These tools bring a new level of convenience and safety to managing food allergies.
In healthcare, AI continues to raise the bar. Machine learning models are improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing the need for risky oral food challenges [3]. As multi-omic analysis becomes more widespread, future diagnostics will likely integrate data such as microbiome profiles, plasma cytokine levels, and T-cell assays to create highly individualized allergy profiles [3].
Building on these advancements, personal health tools are empowering individuals to manage food allergies more effectively. For example, Healify uses AI to turn complex allergen data into practical daily advice. By analyzing inputs from wearables, biometrics, and bloodwork, Healify’s AI health coach, Anna, provides personalized alerts and helps users determine safe consumption levels over time. This integration of biometric data transforms scattered health information into clear, actionable insights, making it easier for users to make informed food choices.
Key Takeaways for Consumers and Professionals
The financial and safety risks of allergen contamination are pushing the food industry to adopt these advanced systems on a large scale. For food industry professionals, AI-powered real-time monitoring helps ensure compliance with FDA and FASTER Act requirements, which added sesame as the ninth major allergen in January 2023 [1]. Non-destructive testing methods not only maintain safety but also keep production lines running smoothly, enhancing both efficiency and reliability.
For consumers, AI-powered tools with molecular pattern recognition can uncover hidden allergens in complex ingredients. When using features like computer vision to scan meals, it’s essential to cross-check results with food labels and consult restaurant staff to account for potential cross-contamination risks [22].
Emerging technologies like federated learning, which trains AI models across institutions without sharing sensitive data, and explainable AI, which clarifies how diagnostic results are determined, are building trust among users while safeguarding privacy [21]. These advancements are making AI allergen detection faster, more accurate, and increasingly tailored to individual needs.
FAQs
How does AI make allergen detection more accurate than traditional methods?
AI is transforming allergen detection by offering a level of precision that traditional methods often struggle to achieve. Techniques like ELISA or skin-prick tests, while widely used, can be slow, costly, and sometimes fail to catch trace allergens - especially in processed foods. On the other hand, AI-powered systems leverage machine learning to analyze protein sequences or ingredient lists, identifying allergens with improved sensitivity and fewer mistakes.
Beyond that, AI combines data from wearables, biometrics, and personal health records to deliver personalized, real-time risk assessments. Take Healify’s AI health coach, for instance - it can analyze your dietary habits and biometric data to alert you to potential allergen exposure before symptoms even appear. By automating complex analyses, boosting accuracy, and offering instant feedback, AI is setting a new standard for reliability and ease in allergen detection.
What challenges do AI allergen detection systems face with regulatory compliance?
AI allergen detection systems face tough hurdles when it comes to navigating food-labeling rules and the growing number of AI-related laws. In the U.S., the FDA requires any claims about major allergens to be supported by validated testing methods. On top of that, risks of cross-contact must be clearly outlined. To meet these strict FDA standards, these systems need to prove they are accurate, reliable, and consistent.
At the same time, AI technologies are held to legal standards emphasizing transparency, explainability, and strong data governance. Companies must ensure their algorithms don’t make misleading claims, provide clear documentation on how results are generated, and maintain detailed audit trails. Platforms like Healify, for instance, need to stay on top of evolving FDA and state-level regulations. This means regularly updating their models, validating their performance, and ensuring their health insights remain both accurate and legally compliant.
How can AI-powered devices help people manage food allergies more effectively?
AI-powered gadgets, like smartphones and wearables, are stepping up as personal assistants for allergy management. By analyzing real-time data - think meal photos, barcode scans, biometrics, and even bloodwork - these devices can pinpoint hidden allergens, flag cross-contamination risks, and recommend safe food options tailored to your specific needs.
On top of that, AI can craft customized meal plans that not only respect your allergy restrictions but also cater to your personal tastes. By tracking symptoms over time, these systems fine-tune their recommendations, making them even more accurate. With real-time alerts, continuous monitoring, and practical advice, managing allergies becomes less stressful and more manageable.
Related Blog Posts
Food allergies affect millions of Americans, with 8% of children and 10% of adults at risk of severe reactions. A single mistake in identifying allergens can lead to life-threatening situations, and undeclared allergens are a major issue for both consumers and food manufacturers. Traditional detection methods like ELISA and PCR are often slow, destructive, and require specialized expertise, leaving room for improvement.
AI-powered allergen detection is changing the game by offering faster, more precise, and non-destructive solutions. Using advanced sensors like hyperspectral imaging and FTIR spectroscopy combined with machine learning, these tools can identify allergens with high accuracy. They’re already being used in manufacturing, restaurants, and even personal devices to improve safety and compliance with FDA regulations.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
How AI is transforming allergen detection with technologies like biosensors and electronic noses.
The role of machine learning models in identifying and quantifying allergens.
How AI tools are improving food safety in manufacturing, restaurants, and personal allergy management.
Key challenges, such as regulatory compliance, data quality, and ethical considerations.
AI allergen detection is reshaping food safety, offering practical solutions for manufacturers and safer choices for consumers.
This Device Can Detect Allergens in Food | Innovation Nation
Technologies That Power AI Allergen Detection

AI Allergen Detection Technologies: Sensors, Accuracy Rates, and Detection Capabilities
AI allergen detection combines advanced sensors, machine learning, and regulatory compliance to deliver quicker, more precise results in food safety.
Sensors and Data Collection Methods
Modern AI systems rely on non-invasive sensors that analyze food without damaging the sample, allowing manufacturers to test products while keeping them market-ready.
Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI): This technique merges photography and spectroscopy to capture hundreds of light wavelengths, revealing hidden allergen traces in food [5].
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy: FTIR uses infrared light to identify molecular bonds in food. By focusing on the 1,700–1,400 cm⁻¹ range, it detects protein-related amide bonds where allergens often reside. In March 2024, researchers Adedeji, Okeke, and Rady developed a smartphone app that uses FTIR data to identify cross-contamination in corn flour [1].
Biosensors: These devices combine biological components, like antibodies, with electronic transducers. A study in June 2023 introduced an impedimetric immunosensor capable of detecting chicken egg ovalbumin at 0.20 µg/mL in just 15 minutes. The system used polyclonal antibodies attached to a gold surface to monitor allergen traces without harming the sample [4].
Electronic Noses (e-noses): These devices use gas sensor arrays to identify volatile organic compounds in food. In early 2026, a study published in Food Control demonstrated that an e-nose paired with a ConvNeXt-AM neural network achieved 93.33% accuracy in detecting spoilage in Hami melons [5].
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Known as the gold standard for processed foods, MS uses liquid chromatography to target proteotypic peptides, offering unmatched sensitivity [6].
These sensors collect precise data, which machine learning models then analyze to generate actionable insights.
Machine Learning Models for Allergen Identification
Once sensor data is collected, machine learning models process and interpret it, identifying allergens with remarkable accuracy. Raw data from sensors is complex, so preprocessing techniques like PCA (Principal Component Analysis) and LDA (Linear Discriminant Analysis) are used to simplify the data and highlight key allergen signals [5].
Classification Models: Algorithms such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests (RF), and k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) are trained on labeled data to identify allergens in new samples [5].
Deep Learning Models: For more complex food compositions, deep learning is increasingly preferred. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), especially 1D-CNNs, excel at analyzing hyperspectral data, detecting allergens across surfaces or within mixtures. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models are ideal for sequential data, such as that from electronic noses, as they track changes over time [5].
These models provide both qualitative insights (identifying which allergen is present) and quantitative measurements (determining the amount, often in parts per million). This capability supports both quality control and adherence to regulatory standards.
Meeting FDA and U.S. Regulatory Requirements
AI allergen detection systems must align with strict U.S. food safety regulations to ensure compliance and consumer safety.
The Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act (FALCPA) of 2004 and the FASTER Act of 2021 require clear labeling of the "Big 9" allergens: milk, eggs, fish, Crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, wheat, peanuts, soybeans, and sesame. Additionally, 21 CFR Part 117 mandates food facilities to implement preventive controls to minimize allergen cross-contact [7][8][9].
While the FDA has set a gluten threshold of 20 ppm for "gluten-free" claims, no general thresholds exist for other allergens. AI systems must be validated to detect even trace amounts that could trigger allergic reactions [9][1]. Traditional methods like ELISA and PCR remain the FDA's primary enforcement tools, so AI technologies need to demonstrate comparable or better accuracy to gain acceptance [9].
"Finding problems before they can potentially harm consumers is a critical element of the FDA's allergen enforcement program." - U.S. Food and Drug Administration [1]
Facilities adopting AI detection technologies must ensure their food safety plans comply with 21 CFR 117.170, which requires reanalysis whenever new hazard information arises [11]. Employee training on allergen cross-contact prevention is also mandatory, regardless of the detection tools in use [10].
Where AI Allergen Detection is Used
With advancements in detection methods, AI is now being used to monitor allergen risks in real time. From factory floors to restaurant kitchens and even personal devices, these systems are transforming how allergen-related challenges are identified and addressed.
Food Manufacturing and Supply Chain Monitoring
Food manufacturers face considerable financial and legal risks from allergen contamination, with recalls potentially costing up to 15% of their annual revenue [1].
AI has stepped in to help. On production lines, tools like computer vision and FTIR spectroscopy monitor operations in real time, while predictive analytics use environmental and historical data to flag potential risks [1][13].
In a significant development, the FDA entered the third phase of its Artificial Intelligence Imported Seafood Pilot program in March 2024. This initiative uses AI and machine learning to enhance the screening of imports at U.S. ports [12]. The FDA has also partnered with industry leaders to establish the Leafy Greens Data Trust, a shared database designed to predict and prevent outbreaks in one of the most contamination-prone food categories [13].
Blockchain and AI-powered traceability systems are replacing outdated paper records. These digital tools can track contaminated food within seconds, allowing manufacturers to quickly address safety concerns [13].
"Smarter food safety is about more than just technology. It's also about simpler, more effective, and modern approaches and processes." - FDA Blueprint [13]
These advancements extend from the manufacturing floor to the dining table, ensuring better safety throughout the supply chain.
Restaurant and Hospitality Applications
Managing allergens in restaurants is no small task. Around 9% of Americans - about 33 million people - live with food allergies [14][15], and cases of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) increased by 377% between 2007 and 2016 [15].
In 2024, Papa Johns teamed up with LiberEat to introduce AI allergen detection technology, offering an extra layer of safety against allergen risks [18].
AI-powered digital menus now allow diners to filter dishes based on specific allergies, reducing the chances of human error and lightening the load on staff. These systems also connect with Point-of-Sale (POS) terminals to flag potential allergen risks during dish customizations, ensuring safer food preparation [16].
At CES 2026, Allergen Alert unveiled a portable "mini lab" created with bioMérieux. This device uses automated immunoassay technology to test for allergens on-site, delivering results in minutes. At a cost of $200, with single-use testing pouches priced under $10 or available via subscription, this tool offers a practical solution for quick allergen detection [14][17].
These innovations are not just limited to restaurants - they complement tools designed for personal allergen management.
Personal Allergy Management Tools
For individuals with food allergies, AI-powered apps and devices are becoming game changers. These tools help users scan food labels, analyze meals, and track allergic reactions in real time.
Handheld devices equipped with AI sensors, such as FTIR and hyperspectral imaging, can detect allergenic proteins without harming the food. This allows users to test their meals on the spot, providing an extra layer of safety [1].
Apps like Healify take allergen management a step further by integrating it into overall health monitoring. Healify’s AI health coach, Anna, uses data from wearables, biometrics, and lifestyle inputs to identify patterns between food intake and allergic reactions, offering tailored advice to help users avoid triggers.
Meanwhile, AI-powered meal-photo counters are achieving accuracy rates between 62% and 99% [19], making allergen management tools more accessible and reliable for millions of people in the U.S. and beyond.
Data Quality, Safety, and Ethics in AI Allergen Detection
AI allergen detection systems are expected to provide fast and precise results while also safeguarding sensitive data. This is particularly important given that one-third of serious food safety risks reported by the FDA involve undeclared allergens [1][9]. Achieving this balance requires handling large datasets responsibly while respecting individual privacy.
Accuracy and Validation Requirements
The reliability of AI-based allergen detection systems depends heavily on the quality of the data used for training. To ensure dependable results, these systems are validated against established gold standards like ELISA, PCR, and Mass Spectrometry [1][9]. For instance, the FDA employs its xMAP assay, which can detect up to 16 allergens in a single test, to oversee food safety and verify labeling accuracy [9].
Key performance metrics for these systems include sensitivity (accurately identifying allergens) and specificity (minimizing false positives) [1]. These tools must be capable of detecting trace amounts of allergens, such as 0.2 mg of protein for peanuts and milk - their respective ED01 thresholds [1].
"Sensor and machine learning coupling in allergen detection is a classic example of artificial intelligence (AI) deployment within the food supply chain with the capability to increase the sustainability of the allergen detection method and reduce the human involvement and response time for reliable feedback." - Akinbode A Adedeji et al. [1]
Manufacturers are encouraged to use multi-method validation to cross-check AI results, such as using two different ELISA kits or combining ELISA with DNA-based PCR methods [9]. Additionally, under 21 CFR part 117, food facilities must implement preventive controls and accurate labeling practices to ensure allergens are properly disclosed [8].
Technical validation creates a foundation for addressing broader concerns like privacy and ethics. By ensuring detection systems are both safe and reliable, manufacturers can foster consumer confidence in AI-driven health solutions.
Privacy and Ethical Design in AI Systems
Beyond achieving technical accuracy, ethical considerations play a crucial role in the design of AI allergen detection systems. These tools, particularly personal health apps, often collect sensitive information about users' diets and medical histories. This creates a challenge: how to build comprehensive datasets without compromising individual privacy [20].
In the U.S., AI systems must adhere to regulations such as the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) and meet manufacturing standards outlined in 21 CFR part 117 [8][9]. Privacy-conscious tools must also secure informed consent and address algorithmic bias [20].
"The price of innovation does not need to be the erosion of fundamental privacy rights." - Elizabeth Denham, Information Commissioner [20]
Transparency is another critical factor. Many AI models function as "black boxes", making it difficult to understand how decisions are made [20]. Developers should adopt principles like "accountability-by-design" and "transparency-by-design" to ensure their systems are interpretable. Tools like SHAP can help make AI decision-making processes clearer for users [21]. Additionally, third-party or government audits can strike a balance between protecting intellectual property and ensuring algorithmic transparency [20].
Algorithmic bias is another pressing issue. To ensure fairness and reliability, training datasets must be diverse. Models built on homogeneous data may fail to perform well for underrepresented groups [21]. For example, systems trained primarily on European populations might yield inaccurate results for Asian or African users, whose allergen sensitization patterns differ [21]. Addressing these gaps is essential for creating equitable and trustworthy AI solutions.
The Future of AI Allergen Detection
AI is reshaping how allergens are detected, shifting the process from reactive to proactive and even personalized. The food industry is embracing cutting-edge digital tools that combine sensors with machine learning to boost both the speed and safety of allergen detection [1]. Technologies like hyperspectral imaging and near-infrared spectroscopy allow manufacturers to pinpoint trace allergens without harming food samples. This makes real-time quality control not only practical but also more cost-efficient [1]. These advancements streamline production and open the door to innovations in personal allergen management.
For consumers, this evolution is just as impactful. Wearable biosensors and smartphone-integrated tools are on the horizon, offering real-time alerts for allergic reactions and enabling quick meal testing [1][2][21]. Imagine snapping a photo of your meal and having computer vision identify ingredients with about 90% accuracy [22]. These tools bring a new level of convenience and safety to managing food allergies.
In healthcare, AI continues to raise the bar. Machine learning models are improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing the need for risky oral food challenges [3]. As multi-omic analysis becomes more widespread, future diagnostics will likely integrate data such as microbiome profiles, plasma cytokine levels, and T-cell assays to create highly individualized allergy profiles [3].
Building on these advancements, personal health tools are empowering individuals to manage food allergies more effectively. For example, Healify uses AI to turn complex allergen data into practical daily advice. By analyzing inputs from wearables, biometrics, and bloodwork, Healify’s AI health coach, Anna, provides personalized alerts and helps users determine safe consumption levels over time. This integration of biometric data transforms scattered health information into clear, actionable insights, making it easier for users to make informed food choices.
Key Takeaways for Consumers and Professionals
The financial and safety risks of allergen contamination are pushing the food industry to adopt these advanced systems on a large scale. For food industry professionals, AI-powered real-time monitoring helps ensure compliance with FDA and FASTER Act requirements, which added sesame as the ninth major allergen in January 2023 [1]. Non-destructive testing methods not only maintain safety but also keep production lines running smoothly, enhancing both efficiency and reliability.
For consumers, AI-powered tools with molecular pattern recognition can uncover hidden allergens in complex ingredients. When using features like computer vision to scan meals, it’s essential to cross-check results with food labels and consult restaurant staff to account for potential cross-contamination risks [22].
Emerging technologies like federated learning, which trains AI models across institutions without sharing sensitive data, and explainable AI, which clarifies how diagnostic results are determined, are building trust among users while safeguarding privacy [21]. These advancements are making AI allergen detection faster, more accurate, and increasingly tailored to individual needs.
FAQs
How does AI make allergen detection more accurate than traditional methods?
AI is transforming allergen detection by offering a level of precision that traditional methods often struggle to achieve. Techniques like ELISA or skin-prick tests, while widely used, can be slow, costly, and sometimes fail to catch trace allergens - especially in processed foods. On the other hand, AI-powered systems leverage machine learning to analyze protein sequences or ingredient lists, identifying allergens with improved sensitivity and fewer mistakes.
Beyond that, AI combines data from wearables, biometrics, and personal health records to deliver personalized, real-time risk assessments. Take Healify’s AI health coach, for instance - it can analyze your dietary habits and biometric data to alert you to potential allergen exposure before symptoms even appear. By automating complex analyses, boosting accuracy, and offering instant feedback, AI is setting a new standard for reliability and ease in allergen detection.
What challenges do AI allergen detection systems face with regulatory compliance?
AI allergen detection systems face tough hurdles when it comes to navigating food-labeling rules and the growing number of AI-related laws. In the U.S., the FDA requires any claims about major allergens to be supported by validated testing methods. On top of that, risks of cross-contact must be clearly outlined. To meet these strict FDA standards, these systems need to prove they are accurate, reliable, and consistent.
At the same time, AI technologies are held to legal standards emphasizing transparency, explainability, and strong data governance. Companies must ensure their algorithms don’t make misleading claims, provide clear documentation on how results are generated, and maintain detailed audit trails. Platforms like Healify, for instance, need to stay on top of evolving FDA and state-level regulations. This means regularly updating their models, validating their performance, and ensuring their health insights remain both accurate and legally compliant.
How can AI-powered devices help people manage food allergies more effectively?
AI-powered gadgets, like smartphones and wearables, are stepping up as personal assistants for allergy management. By analyzing real-time data - think meal photos, barcode scans, biometrics, and even bloodwork - these devices can pinpoint hidden allergens, flag cross-contamination risks, and recommend safe food options tailored to your specific needs.
On top of that, AI can craft customized meal plans that not only respect your allergy restrictions but also cater to your personal tastes. By tracking symptoms over time, these systems fine-tune their recommendations, making them even more accurate. With real-time alerts, continuous monitoring, and practical advice, managing allergies becomes less stressful and more manageable.
Related Blog Posts
Finalmente toma el control de tu salud

Finalmente toma el control de tu salud

Finalmente toma el control de tu salud





