Improve your health
Improve your health
Improve your health
18 de diciembre de 2025
Requisitos de Auditoría de TI de Salud para 2025 Explicados


Los requisitos de auditoría de TI de salud para 2025 son más estrictos que nunca, introduciendo cambios importantes para garantizar una mejor ciberseguridad y cumplimiento en la atención médica. Esto es lo que necesitas saber:
Actualizaciones de la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA: La mayoría de los requisitos previamente opcionales ahora son obligatorios. Se requieren evaluaciones de riesgo anuales, cifrado, autenticación multifactor y exploraciones regulares de vulnerabilidad.
Compartición de Datos con Terceros: Los asociados comerciales deben realizar análisis de riesgos por escrito anualmente y seguir estrictas salvaguardias. Los Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) válidos son obligatorios para todos los proveedores que manejen Información de Salud Protegida (PHI).
ONC Regla Final del Acta Cures: Los sistemas de TI de salud certificados deben usar APIs estandarizadas para compartir datos y cumplir con los nuevos estándares de interoperabilidad como USCDI v6.
Expansión del Ámbito de la Auditoría: Los reguladores ahora revisarán todas las salvaguardias críticas, abordando las brechas en auditorías previas que solo cubrían 8 de los 180 requisitos de HIPAA.
Aplicaciones de Salud impulsadas por IA: Los nuevos estándares exigen un manejo seguro de PHI, documentación detallada y transparencia en las operaciones de IA.
Fechas Clave:
6 de enero de 2025: Publicación de las actualizaciones de la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA.
20 de mayo de 2025: Se espera que se publiquen las pautas ampliadas de auditoría.
1 de octubre de 2025: Entra en vigor la Regla Final HTI-4 de ONC.
Las organizaciones deben actuar ahora para alinearse con estas actualizaciones, ya que el incumplimiento conlleva severas sanciones. El enfoque está en salvaguardas más fuertes, una supervisión más estricta de los proveedores y una mayor preparación para las auditorías.
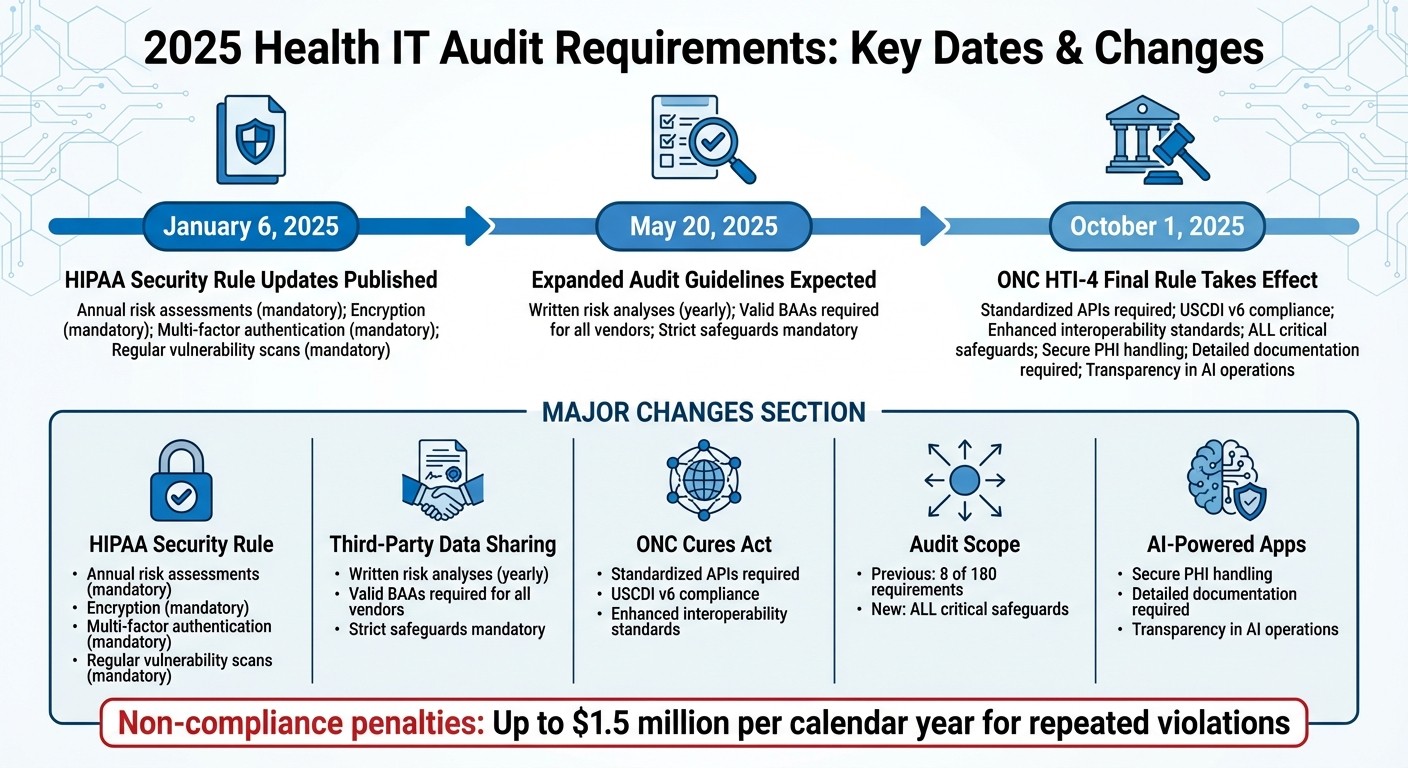
Cronograma de Requisitos de Auditoría de TI de Salud 2025 y Cambios Clave
Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA - Cambios Importantes para 2025
Marcos Regulatorios Principales para 2025
A medida que avanzamos hacia 2025, mantenerse en cumplimiento con las regulaciones de auditoría de TI de salud significa alinearse con los estándares actualizados en el Acta Cures de ONC y la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA. A continuación se presentan las actualizaciones clave y cambios procedimentales que las organizaciones deben abordar.
ONC Actualizaciones de la Regla Final del Acta Cures
La Normativa Final de Datos de Salud, Tecnología e Interoperabilidad: Prescripción Electrónica, Beneficio de Prescripción en Tiempo Real y Autorización Previa Electrónica (HTI-4) entra oficialmente en vigor el 1 de octubre de 2025 [3]. Esta normativa introduce nuevos requisitos de certificación para los sistemas de TI de salud, centrándose en la autorización aprobada electrónicamente, la prescripción electrónica, y la información de beneficio de prescripción en tiempo real [3].
Un cambio importante es el requisito para que los sistemas de TI de salud intercambien datos clínicos y administrativos con los pagadores usando APIs estandarizadas [3]. Durante las auditorías, se evaluarán los EHRes certificados para asegurarse de que apoyan estos procesos actualizados y cumplen con los nuevos estándares de intercambio de datos.
Las directrices de interoperabilidad más recientes - USCDI v6 (publicado en julio de 2025) y los Estándares Aprobados de SVAP 2025 (publicados en junio de 2025) - sirven como referencia para las auditorías. Estos estándares garantizan que los sistemas están implementando las prácticas más actuales de compartir datos [4].
Se presentó un problema temporal cuando una interrupción en la financiación gubernamental desde el 1 de octubre hasta el 12 de noviembre de 2025 llevó a ASTP/ONC a emitir avisos de discreción en la aplicación de normas. Estos avisos proporcionaron flexibilidad para criterios de certificación específicos y plazos de declaración durante este periodo [4]. Los auditores tendrán que considerar este ajuste al revisar el cumplimiento de las actividades que ocurran dentro de ese periodo de tiempo.
Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA: Controles de Auditoría
Bajo la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, las entidades cubiertas y asociados comerciales deben implementar controles de auditoría para monitorear el acceso y las actividades dentro de los sistemas ePHI (§164.312(b)) [5][6]. Estos controles requieren el uso de herramientas de hardware, software o procedimientos para registrar detalles como quién accedió a la información, qué fue accesado y cualquier acción realizada.
Además, las organizaciones están obligadas a retener políticas y procedimientos por escrito durante seis años desde su creación o fecha efectiva. Esta norma de conservación aplica a todas las acciones, actividades y evaluaciones requeridas por la Regla de Seguridad. Crea un rastro de auditoría robusto para que los reguladores examinen durante revisiones de cumplimiento.
Estos requisitos claros de control de auditoría también establecen el fundamento para evaluar cómo se gestiona el intercambio de datos con terceros, asegurando que todos los procesos se alineen con las expectativas regulatorias.
Requisitos de Compartición de Datos con Terceros
Hacer cumplir el cumplimiento con socios externos es tan importante como mantener controles de auditoría internos. Cuando se comparte Información de Salud Protegida (PHI), los sistemas de TI de salud deben asegurarse de que los Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) estén en su lugar, exigiendo a los proveedores terceros cumplir con las estrictas salvaguardias de HIPAA.
Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs)
HIPAA requiere que cualquier proveedor externo involucrado en la creación, recepción, mantenimiento o transmisión de PHI para una organización de atención médica firme un BAA [7][8]. Estos acuerdos aseguran que los proveedores - y sus subcontratistas - adhieran a las estrictas normas de HIPAA. Esto incluye:
Usar PHI estrictamente para sus propósitos previstos.
Implementar las salvaguardias necesarias para proteger los datos sensibles.
Informar puntualmente cualquier violación o divulgación no autorizada [7][8].
Los reguladores verifican durante las auditorías que cada relación con un proveedor que implique PHI está respaldada por un BAA válido, y que el acuerdo cumple con las regulaciones actuales de HIPAA. Este paso es crucial para mantener la responsabilidad y proteger la información del paciente.
Cómo Prepararse para las Auditorías de TI de Salud 2025
Prepararse para las auditorías de TI de salud de 2025 significa adoptar una postura proactiva para abordar los requisitos de cumplimiento. El objetivo es establecer una base sólida realizando evaluaciones de riesgos, actualizando políticas y procedimientos, y realizando auditorías internas regulares. Aquí un vistazo más de cerca a estos pasos críticos.
Realizar Evaluaciones de Riesgo
Bajo los mandatos actualizados de HIPAA, la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA requiere que las organizaciones de salud y sus asociados comerciales realicen evaluaciones regulares de riesgos [9][10]. Estas evaluaciones tienen como objetivo identificar riesgos potenciales y vulnerabilidades que podrían comprometer la confidencialidad, integridad y disponibilidad de la información de salud protegida electrónica (ePHI) [9][10].
En septiembre de 2025, la Oficina del Coordinador Nacional para la Tecnología de la Información de Salud (ONC) y la Oficina de Derechos Civiles del HHS (OCR) introdujeron la Versión 3.6 de la Herramienta de Evaluación de Riesgos de Seguridad (SRA). Esta versión incluye características como un nuevo botón de confirmación de evaluación para registrar las fechas de "revisión por", junto con el nombre de usuario del aprobador y la fecha de aprobación para fines de auditoría. La herramienta también alinea su escala de riesgo con la puntuación de NIST y mejora los informes específicos de sección, simplificando el proceso para que los proveedores pequeños y medianos documenten sus evaluaciones de riesgo requeridas por HIPAA [9].
Las evaluaciones de riesgos también deben abordar la gestión de activos y proveedores para identificar dónde se almacena, procesa o transmite ePHI - especialmente por terceros [9]. Una vez identificados los riesgos, implementa medidas de seguridad apropiadas para reducirlos a niveles aceptables [10]. Asegúrate de guardar e imprimir informes detallados generados a partir de las evaluaciones para mantener una documentación completa para las auditorías [9].
Actualizar Políticas y Procedimientos
Revisa tus políticas y procedimientos para alinearlos con las modificaciones de 2025 a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, que enfatizan medidas de ciberseguridad más fuertes para ePHI [2]. Estas actualizaciones cubren salvaguardias administrativas, técnicas y organizacionales, introduciendo nuevos estándares como:
Inventario de Activos Tecnológicos
Gestión de Parches
Auditorías de Cumplimiento
Cifrado y Descifrado
Gestión de Configuración
Controles de Registro de Auditoría y del Sistema
Autenticación
Gestión de Vulnerabilidades
Respaldos de Datos
Revisa tu documentación actual en comparación con estos estándares actualizados y realiza los ajustes necesarios. Las políticas que fueron suficientes en 2023 pueden no cumplir con los requisitos más estrictos de 2025. Presta especial atención a las áreas que involucran controles de auditoría y gestión de proveedores, ya que estas son fuentes comunes de brechas de cumplimiento.
Realizar Auditorías Internas Regulares
Para mantener el cumplimiento, las organizaciones necesitan establecer medidas para prevenir, detectar y abordar violaciones de seguridad como parte de su proceso de gestión de seguridad [10]. Las auditorías internas regulares deben incluir la revisión de registros de actividad del sistema, como registros de auditoría, informes de acceso e informes de seguimiento de incidentes de seguridad [10].
La Oficina de Derechos Civiles del HHS (OCR) ha propuesto actualizaciones a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, incluyendo un nuevo estándar de “Auditoria de Cumplimiento” bajo salvaguardias administrativas y cambios a “Controles de Registro de Auditoría y del Sistema” bajo salvaguardias técnicas [2]. Estas actualizaciones abordan el creciente número de violaciones y ciberataques, así como las deficiencias comunes de cumplimiento [2].
Configure sistemas para rastrear y revisar actividades relacionadas con ePHI [5]. Realiza evaluaciones técnicas y no técnicas de manera regular, especialmente después de cualquier cambio en tu entorno operativo que pueda afectar la seguridad de ePHI. Mantén registros de auditoría detallados para demostrar cumplimiento durante las auditorías [10].
Impacto en Aplicaciones de Salud Impulsadas por IA
Las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA como Healify ahora están bajo un escrutinio más estricto debido a las actualizaciones de HIPAA de 2025, que enfatizan medidas robustas de protección de datos. Estas actualizaciones se centran fuertemente en tecnologías emergentes, incluida la IA, requiriendo salvaguardias más fuertes para proteger la Información de Salud Protegida (PHI) mientras se adhiere al Estándar Mínimo Necesario de HIPAA.
En enero de 2025, los cambios propuestos a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA destacaron específicamente la necesidad de abordar nuevas tecnologías como la Inteligencia Artificial [2]. Esto refleja una creciente conciencia entre los reguladores sobre los desafíos únicos que la IA plantea al manejar datos de salud. La naturaleza autónoma de los sistemas de IA introduce riesgos, como la exposición no intencional de PHI o posibles violaciones de HIPAA [11].
Cumplir con los Estándares de Cumplimiento para el Manejo de Datos
Para alinearse con los requisitos de 2025, las aplicaciones de salud basadas en IA deben adoptar salvaguardias técnicas avanzadas. Por ejemplo, Mississippi State University desarrolló recientemente un marco de IA Agento compatible con HIPAA que incorpora controles de acceso dinámico, sanitización de PHI y registros de auditoría inmutables. Este marco logró un puntaje F1 del 98.4% en redacción de PHI, demostrando su efectividad [11].
Al integrar datos de múltiples fuentes, las aplicaciones deben asegurar Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) en cada punto de acceso para cerrar brechas de cumplimiento. Seguir prácticas de BAA establecidas garantiza una integración adecuada de proveedores. Además, se deben implementar controles de acceso dinámico para gestionar el acceso a PHI en función de roles de usuario y factores contextuales, restringiendo la información sensible solo al personal o sistemas autorizados [11].
Los estándares propuestos para "Inventario de Activos Tecnológicos", "Gestión de Parches" y "Auditorías de Cumplimiento" bajo la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA también exigen documentación detallada para todos los sistemas que procesan datos de salud [2]. Esto incluye el seguimiento de versiones de modelos de IA, fuentes de datos de entrenamiento y procesos de toma de decisiones - esencial para aplicaciones que brindan recomendaciones de salud personalizadas basadas en datos biométricos.
Construir Confianza del Usuario a través de la Transparencia
Fuertes salvaguardias técnicas son clave para fomentar la transparencia y construir la confianza del usuario. A medida que las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA manejan datos cada vez más sensibles, la comunicación clara sobre las prácticas de manejo de datos se vuelve esencial. Subash Neupane, investigador de la Universidad Estatal de Mississippi, enfatizó:
"La integración de IA en la atención médica exige un estricto cumplimiento de marcos regulatorios como HIPAA, particularmente al manejar Información de Salud Protegida" [11].
La legislación como la Ley de la Asamblea de California 489, introducida en 2025, subraya aún más la importancia de la transparencia. Este proyecto de ley requiere que las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA divulguen claramente sus capacidades de IA y prohíbe afirmaciones engañosas sobre interacciones con IA, como implicar supervisión por profesionales médicos licenciados cuando no existe [12]. La tergiversación erosiona la confianza, por lo que es crítico para las aplicaciones ser francas sobre lo que su IA puede - y no puede - hacer.
Además, la Oficina de Derechos Civiles (OCR) ha ampliado su programa de auditoría para incluir salvaguardias físicas y técnicas. Este cambio sigue a una auditoría del OIG el 21 de noviembre de 2024, que reveló que solo se estaban evaluando 8 de los 180 requisitos de la Regla de HIPAA [1]. Los registros de auditoría completos no solo ayudan a cumplir con las demandas regulatorias sino que también mejoran la confianza del usuario al documentar cada instancia de acceso a datos y recomendaciones impulsadas por IA. La transparencia en estos procesos es una piedra angular para mantener tanto el cumplimiento como la credibilidad.
Conclusión
Las actualizaciones de 2025 a los requisitos de auditoría de TI de salud marcan un punto de inflexión para cómo las organizaciones manejan el cumplimiento. El 6 de enero de 2025, el Departamento de Salud y Servicios Humanos propuso cambios a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, citando "incrementos significativos en violaciones y ciberataques" junto con "cumplimiento inconsistente" entre las entidades reguladas [2]. Estas actualizaciones hacen que la estricta adhesión a las reglas sea una necesidad.
Un reporte del OIG destacó brechas críticas en las auditorías [1], y con un ámbito ampliado programado para el 20 de mayo de 2025, los esfuerzos mínimos de cumplimiento ya no serán suficientes.
Añadiendo a estos mandatos internos, el intercambio seguro de datos con terceros ha cambiado de ser una práctica recomendada a un requisito regulatorio. Las entidades cubiertas ahora deben asegurarse de que cualquier tercero con el que trabajen cumpla con las salvaguardias técnicas establecidas [2]. Esto significa que las organizaciones deben revisar sus Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales y realizar evaluaciones de riesgo exhaustivas de proveedores como parte de sus esfuerzos de cumplimiento.
Para las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA como Healify -que proporciona orientación personalizada las 24/7- estos cambios exigen una acción rápida. Los desarrolladores y organizaciones necesitan prepararse para costos más altos relacionados con auditorías de cumplimiento, revisiones de políticas y capacitación de la fuerza laboral [2]. Las penalizaciones por incumplimiento siguen siendo severas, con multas que pueden llegar hasta $1.5 millones por año calendario por violaciones repetidas de la misma disposición [8].
Los reguladores han dejado claro: actuar no puede esperar. Retrasar el cumplimiento supone riesgos serios, especialmente a medida que el HHS planea intensificar las actividades de aplicación en septiembre de 2025 para abordar el bloqueo de información [4]. La ventana para lograr el cumplimiento está cerrándose rápidamente. Estos desarrollos enfatizan una conclusión clave: en 2025, el cumplimiento no solo es esencial, está evolucionando a un ritmo rápido.
Preguntas Frecuentes
¿Cuáles son las principales actualizaciones de la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA de 2025?
Las actualizaciones de 2025 a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA marcan un avance importante en el fortalecimiento de la seguridad de los datos y garantizar el cumplimiento. Uno de los cambios más notables es el cambio de salvaguardias "abordables" a obligatorias. Esto significa que cada organización ahora debe implementar estas medidas sin excepciones. Además, los asociados comerciales ahora están obligados a informar directamente las violaciones e incidentes de seguridad a la Oficina de Derechos Civiles (OCR). Otra actualización crítica es el requisito universal de cifrar toda la información de salud protegida electrónica (ePHI), ya sea que se almacene o se transmita.
Las actualizaciones también introducen varias otras medidas esenciales, incluyendo autenticación multifactorial obligatoria, gestión regular de parches, pruebas de penetración rutinarias y análisis de riesgos más detallados. Estas evaluaciones de riesgos están diseñadas para identificar vulnerabilidades y evaluar amenazas potenciales a ePHI. Al alinearse con el Marco de Ciberseguridad de NIST, estas actualizaciones tienen como objetivo abordar los crecientes riesgos planteados por ciberataques como ransomware. En conjunto, estos cambios establecen estándares más estrictos para proteger los datos del paciente y asegurar la responsabilidad, especialmente al compartir datos con terceros.
¿Qué cambios traen los requisitos de auditoría de 2025 a la compartición de datos con terceros en la TI de salud?
Los requisitos de auditoría de 2025 traen regulaciones más estrictas para compartir datos con terceros en la TI de salud. Bajo estas nuevas reglas, las organizaciones deben establecer controles de auditoría detallados y mantener registros completos de cada instancia de acceso y transferencia de datos. Además, los asociados comerciales de terceros ahora deben adherirse a los mismos estándares de seguridad que los proveedores de atención médica, asegurando que la información de salud sensible permanezca protegida.
Estos cambios están diseñados para aumentar la transparencia y la responsabilidad, protegiendo la información de salud protegida electrónica (ePHI) mientras se alinea con las regulaciones federales. Mantenerse al día con estos requisitos es crucial para preservar la confianza y evitar posibles sanciones.
¿Qué pasos deben seguir los desarrolladores de aplicaciones de salud de IA para cumplir con los requisitos de auditoría de 2025?
Para cumplir con los requisitos de auditoría de TI de salud de 2025, los desarrolladores de aplicaciones de salud de IA necesitan una estrategia bien organizada. Aquí se explica cómo comenzar:
Familiarízate con las Regulaciones: Identifica las leyes federales y estatales relevantes para tu aplicación, como HIPAA, la Ley HITECH y regulaciones más recientes centradas en la IA como la AB 489 de California. Si tu aplicación maneja datos transfronterizos, marcos como GDPR también deben estar en tu radar.
Realizar una Evaluación de Riesgos: Identifica vulnerabilidades en tu aplicación - ya sean técnicas, administrativas o físicas. Luego, implementa salvaguardias como cifrado, controles de acceso basado en roles y registros de auditoría. Asigna un oficial de cumplimiento para supervisar estas medidas y asegurarte de que todo se mantenga en camino.
Fortalecer las Relaciones con Proveedores: Usa Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) para confirmar que los proveedores externos cumplan con tus requisitos de seguridad. Mapea cómo los datos sensibles, como las biométricas o los resultados de laboratorio, se mueven a través de sistemas de terceros para identificar y abordar posibles riesgos.
Compromiso con el Monitoreo y Formación Continuos: Utiliza herramientas para detectar actividad sospechosa, programa auditorías rutinarias y ofrece al personal formación regular sobre protocolos de privacidad y ética de IA.
Antes de lanzar tu aplicación, valida su cumplimiento a través de pruebas funcionales y regulatorias. Asegúrate de que los resultados de IA sean fáciles de entender, estén libres de sesgo y estén claramente etiquetados para que los usuarios sepan que están interactuando con un algoritmo. Después del lanzamiento, mantén el cumplimiento auditando regularmente, actualizando salvaguardias cada vez que cambien los sistemas y manteniendo registros exhaustivos para cumplir con los requisitos de auditoría. Estos pasos no solo protegen los datos del paciente, sino que también ayudan a ofrecer un cuidado personalizado y seguro.
Entradas de Blog Relacionadas
Los requisitos de auditoría de TI de salud para 2025 son más estrictos que nunca, introduciendo cambios importantes para garantizar una mejor ciberseguridad y cumplimiento en la atención médica. Esto es lo que necesitas saber:
Actualizaciones de la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA: La mayoría de los requisitos previamente opcionales ahora son obligatorios. Se requieren evaluaciones de riesgo anuales, cifrado, autenticación multifactor y exploraciones regulares de vulnerabilidad.
Compartición de Datos con Terceros: Los asociados comerciales deben realizar análisis de riesgos por escrito anualmente y seguir estrictas salvaguardias. Los Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) válidos son obligatorios para todos los proveedores que manejen Información de Salud Protegida (PHI).
ONC Regla Final del Acta Cures: Los sistemas de TI de salud certificados deben usar APIs estandarizadas para compartir datos y cumplir con los nuevos estándares de interoperabilidad como USCDI v6.
Expansión del Ámbito de la Auditoría: Los reguladores ahora revisarán todas las salvaguardias críticas, abordando las brechas en auditorías previas que solo cubrían 8 de los 180 requisitos de HIPAA.
Aplicaciones de Salud impulsadas por IA: Los nuevos estándares exigen un manejo seguro de PHI, documentación detallada y transparencia en las operaciones de IA.
Fechas Clave:
6 de enero de 2025: Publicación de las actualizaciones de la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA.
20 de mayo de 2025: Se espera que se publiquen las pautas ampliadas de auditoría.
1 de octubre de 2025: Entra en vigor la Regla Final HTI-4 de ONC.
Las organizaciones deben actuar ahora para alinearse con estas actualizaciones, ya que el incumplimiento conlleva severas sanciones. El enfoque está en salvaguardas más fuertes, una supervisión más estricta de los proveedores y una mayor preparación para las auditorías.

Cronograma de Requisitos de Auditoría de TI de Salud 2025 y Cambios Clave
Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA - Cambios Importantes para 2025
Marcos Regulatorios Principales para 2025
A medida que avanzamos hacia 2025, mantenerse en cumplimiento con las regulaciones de auditoría de TI de salud significa alinearse con los estándares actualizados en el Acta Cures de ONC y la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA. A continuación se presentan las actualizaciones clave y cambios procedimentales que las organizaciones deben abordar.
ONC Actualizaciones de la Regla Final del Acta Cures
La Normativa Final de Datos de Salud, Tecnología e Interoperabilidad: Prescripción Electrónica, Beneficio de Prescripción en Tiempo Real y Autorización Previa Electrónica (HTI-4) entra oficialmente en vigor el 1 de octubre de 2025 [3]. Esta normativa introduce nuevos requisitos de certificación para los sistemas de TI de salud, centrándose en la autorización aprobada electrónicamente, la prescripción electrónica, y la información de beneficio de prescripción en tiempo real [3].
Un cambio importante es el requisito para que los sistemas de TI de salud intercambien datos clínicos y administrativos con los pagadores usando APIs estandarizadas [3]. Durante las auditorías, se evaluarán los EHRes certificados para asegurarse de que apoyan estos procesos actualizados y cumplen con los nuevos estándares de intercambio de datos.
Las directrices de interoperabilidad más recientes - USCDI v6 (publicado en julio de 2025) y los Estándares Aprobados de SVAP 2025 (publicados en junio de 2025) - sirven como referencia para las auditorías. Estos estándares garantizan que los sistemas están implementando las prácticas más actuales de compartir datos [4].
Se presentó un problema temporal cuando una interrupción en la financiación gubernamental desde el 1 de octubre hasta el 12 de noviembre de 2025 llevó a ASTP/ONC a emitir avisos de discreción en la aplicación de normas. Estos avisos proporcionaron flexibilidad para criterios de certificación específicos y plazos de declaración durante este periodo [4]. Los auditores tendrán que considerar este ajuste al revisar el cumplimiento de las actividades que ocurran dentro de ese periodo de tiempo.
Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA: Controles de Auditoría
Bajo la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, las entidades cubiertas y asociados comerciales deben implementar controles de auditoría para monitorear el acceso y las actividades dentro de los sistemas ePHI (§164.312(b)) [5][6]. Estos controles requieren el uso de herramientas de hardware, software o procedimientos para registrar detalles como quién accedió a la información, qué fue accesado y cualquier acción realizada.
Además, las organizaciones están obligadas a retener políticas y procedimientos por escrito durante seis años desde su creación o fecha efectiva. Esta norma de conservación aplica a todas las acciones, actividades y evaluaciones requeridas por la Regla de Seguridad. Crea un rastro de auditoría robusto para que los reguladores examinen durante revisiones de cumplimiento.
Estos requisitos claros de control de auditoría también establecen el fundamento para evaluar cómo se gestiona el intercambio de datos con terceros, asegurando que todos los procesos se alineen con las expectativas regulatorias.
Requisitos de Compartición de Datos con Terceros
Hacer cumplir el cumplimiento con socios externos es tan importante como mantener controles de auditoría internos. Cuando se comparte Información de Salud Protegida (PHI), los sistemas de TI de salud deben asegurarse de que los Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) estén en su lugar, exigiendo a los proveedores terceros cumplir con las estrictas salvaguardias de HIPAA.
Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs)
HIPAA requiere que cualquier proveedor externo involucrado en la creación, recepción, mantenimiento o transmisión de PHI para una organización de atención médica firme un BAA [7][8]. Estos acuerdos aseguran que los proveedores - y sus subcontratistas - adhieran a las estrictas normas de HIPAA. Esto incluye:
Usar PHI estrictamente para sus propósitos previstos.
Implementar las salvaguardias necesarias para proteger los datos sensibles.
Informar puntualmente cualquier violación o divulgación no autorizada [7][8].
Los reguladores verifican durante las auditorías que cada relación con un proveedor que implique PHI está respaldada por un BAA válido, y que el acuerdo cumple con las regulaciones actuales de HIPAA. Este paso es crucial para mantener la responsabilidad y proteger la información del paciente.
Cómo Prepararse para las Auditorías de TI de Salud 2025
Prepararse para las auditorías de TI de salud de 2025 significa adoptar una postura proactiva para abordar los requisitos de cumplimiento. El objetivo es establecer una base sólida realizando evaluaciones de riesgos, actualizando políticas y procedimientos, y realizando auditorías internas regulares. Aquí un vistazo más de cerca a estos pasos críticos.
Realizar Evaluaciones de Riesgo
Bajo los mandatos actualizados de HIPAA, la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA requiere que las organizaciones de salud y sus asociados comerciales realicen evaluaciones regulares de riesgos [9][10]. Estas evaluaciones tienen como objetivo identificar riesgos potenciales y vulnerabilidades que podrían comprometer la confidencialidad, integridad y disponibilidad de la información de salud protegida electrónica (ePHI) [9][10].
En septiembre de 2025, la Oficina del Coordinador Nacional para la Tecnología de la Información de Salud (ONC) y la Oficina de Derechos Civiles del HHS (OCR) introdujeron la Versión 3.6 de la Herramienta de Evaluación de Riesgos de Seguridad (SRA). Esta versión incluye características como un nuevo botón de confirmación de evaluación para registrar las fechas de "revisión por", junto con el nombre de usuario del aprobador y la fecha de aprobación para fines de auditoría. La herramienta también alinea su escala de riesgo con la puntuación de NIST y mejora los informes específicos de sección, simplificando el proceso para que los proveedores pequeños y medianos documenten sus evaluaciones de riesgo requeridas por HIPAA [9].
Las evaluaciones de riesgos también deben abordar la gestión de activos y proveedores para identificar dónde se almacena, procesa o transmite ePHI - especialmente por terceros [9]. Una vez identificados los riesgos, implementa medidas de seguridad apropiadas para reducirlos a niveles aceptables [10]. Asegúrate de guardar e imprimir informes detallados generados a partir de las evaluaciones para mantener una documentación completa para las auditorías [9].
Actualizar Políticas y Procedimientos
Revisa tus políticas y procedimientos para alinearlos con las modificaciones de 2025 a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, que enfatizan medidas de ciberseguridad más fuertes para ePHI [2]. Estas actualizaciones cubren salvaguardias administrativas, técnicas y organizacionales, introduciendo nuevos estándares como:
Inventario de Activos Tecnológicos
Gestión de Parches
Auditorías de Cumplimiento
Cifrado y Descifrado
Gestión de Configuración
Controles de Registro de Auditoría y del Sistema
Autenticación
Gestión de Vulnerabilidades
Respaldos de Datos
Revisa tu documentación actual en comparación con estos estándares actualizados y realiza los ajustes necesarios. Las políticas que fueron suficientes en 2023 pueden no cumplir con los requisitos más estrictos de 2025. Presta especial atención a las áreas que involucran controles de auditoría y gestión de proveedores, ya que estas son fuentes comunes de brechas de cumplimiento.
Realizar Auditorías Internas Regulares
Para mantener el cumplimiento, las organizaciones necesitan establecer medidas para prevenir, detectar y abordar violaciones de seguridad como parte de su proceso de gestión de seguridad [10]. Las auditorías internas regulares deben incluir la revisión de registros de actividad del sistema, como registros de auditoría, informes de acceso e informes de seguimiento de incidentes de seguridad [10].
La Oficina de Derechos Civiles del HHS (OCR) ha propuesto actualizaciones a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, incluyendo un nuevo estándar de “Auditoria de Cumplimiento” bajo salvaguardias administrativas y cambios a “Controles de Registro de Auditoría y del Sistema” bajo salvaguardias técnicas [2]. Estas actualizaciones abordan el creciente número de violaciones y ciberataques, así como las deficiencias comunes de cumplimiento [2].
Configure sistemas para rastrear y revisar actividades relacionadas con ePHI [5]. Realiza evaluaciones técnicas y no técnicas de manera regular, especialmente después de cualquier cambio en tu entorno operativo que pueda afectar la seguridad de ePHI. Mantén registros de auditoría detallados para demostrar cumplimiento durante las auditorías [10].
Impacto en Aplicaciones de Salud Impulsadas por IA
Las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA como Healify ahora están bajo un escrutinio más estricto debido a las actualizaciones de HIPAA de 2025, que enfatizan medidas robustas de protección de datos. Estas actualizaciones se centran fuertemente en tecnologías emergentes, incluida la IA, requiriendo salvaguardias más fuertes para proteger la Información de Salud Protegida (PHI) mientras se adhiere al Estándar Mínimo Necesario de HIPAA.
En enero de 2025, los cambios propuestos a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA destacaron específicamente la necesidad de abordar nuevas tecnologías como la Inteligencia Artificial [2]. Esto refleja una creciente conciencia entre los reguladores sobre los desafíos únicos que la IA plantea al manejar datos de salud. La naturaleza autónoma de los sistemas de IA introduce riesgos, como la exposición no intencional de PHI o posibles violaciones de HIPAA [11].
Cumplir con los Estándares de Cumplimiento para el Manejo de Datos
Para alinearse con los requisitos de 2025, las aplicaciones de salud basadas en IA deben adoptar salvaguardias técnicas avanzadas. Por ejemplo, Mississippi State University desarrolló recientemente un marco de IA Agento compatible con HIPAA que incorpora controles de acceso dinámico, sanitización de PHI y registros de auditoría inmutables. Este marco logró un puntaje F1 del 98.4% en redacción de PHI, demostrando su efectividad [11].
Al integrar datos de múltiples fuentes, las aplicaciones deben asegurar Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) en cada punto de acceso para cerrar brechas de cumplimiento. Seguir prácticas de BAA establecidas garantiza una integración adecuada de proveedores. Además, se deben implementar controles de acceso dinámico para gestionar el acceso a PHI en función de roles de usuario y factores contextuales, restringiendo la información sensible solo al personal o sistemas autorizados [11].
Los estándares propuestos para "Inventario de Activos Tecnológicos", "Gestión de Parches" y "Auditorías de Cumplimiento" bajo la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA también exigen documentación detallada para todos los sistemas que procesan datos de salud [2]. Esto incluye el seguimiento de versiones de modelos de IA, fuentes de datos de entrenamiento y procesos de toma de decisiones - esencial para aplicaciones que brindan recomendaciones de salud personalizadas basadas en datos biométricos.
Construir Confianza del Usuario a través de la Transparencia
Fuertes salvaguardias técnicas son clave para fomentar la transparencia y construir la confianza del usuario. A medida que las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA manejan datos cada vez más sensibles, la comunicación clara sobre las prácticas de manejo de datos se vuelve esencial. Subash Neupane, investigador de la Universidad Estatal de Mississippi, enfatizó:
"La integración de IA en la atención médica exige un estricto cumplimiento de marcos regulatorios como HIPAA, particularmente al manejar Información de Salud Protegida" [11].
La legislación como la Ley de la Asamblea de California 489, introducida en 2025, subraya aún más la importancia de la transparencia. Este proyecto de ley requiere que las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA divulguen claramente sus capacidades de IA y prohíbe afirmaciones engañosas sobre interacciones con IA, como implicar supervisión por profesionales médicos licenciados cuando no existe [12]. La tergiversación erosiona la confianza, por lo que es crítico para las aplicaciones ser francas sobre lo que su IA puede - y no puede - hacer.
Además, la Oficina de Derechos Civiles (OCR) ha ampliado su programa de auditoría para incluir salvaguardias físicas y técnicas. Este cambio sigue a una auditoría del OIG el 21 de noviembre de 2024, que reveló que solo se estaban evaluando 8 de los 180 requisitos de la Regla de HIPAA [1]. Los registros de auditoría completos no solo ayudan a cumplir con las demandas regulatorias sino que también mejoran la confianza del usuario al documentar cada instancia de acceso a datos y recomendaciones impulsadas por IA. La transparencia en estos procesos es una piedra angular para mantener tanto el cumplimiento como la credibilidad.
Conclusión
Las actualizaciones de 2025 a los requisitos de auditoría de TI de salud marcan un punto de inflexión para cómo las organizaciones manejan el cumplimiento. El 6 de enero de 2025, el Departamento de Salud y Servicios Humanos propuso cambios a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA, citando "incrementos significativos en violaciones y ciberataques" junto con "cumplimiento inconsistente" entre las entidades reguladas [2]. Estas actualizaciones hacen que la estricta adhesión a las reglas sea una necesidad.
Un reporte del OIG destacó brechas críticas en las auditorías [1], y con un ámbito ampliado programado para el 20 de mayo de 2025, los esfuerzos mínimos de cumplimiento ya no serán suficientes.
Añadiendo a estos mandatos internos, el intercambio seguro de datos con terceros ha cambiado de ser una práctica recomendada a un requisito regulatorio. Las entidades cubiertas ahora deben asegurarse de que cualquier tercero con el que trabajen cumpla con las salvaguardias técnicas establecidas [2]. Esto significa que las organizaciones deben revisar sus Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales y realizar evaluaciones de riesgo exhaustivas de proveedores como parte de sus esfuerzos de cumplimiento.
Para las aplicaciones de salud impulsadas por IA como Healify -que proporciona orientación personalizada las 24/7- estos cambios exigen una acción rápida. Los desarrolladores y organizaciones necesitan prepararse para costos más altos relacionados con auditorías de cumplimiento, revisiones de políticas y capacitación de la fuerza laboral [2]. Las penalizaciones por incumplimiento siguen siendo severas, con multas que pueden llegar hasta $1.5 millones por año calendario por violaciones repetidas de la misma disposición [8].
Los reguladores han dejado claro: actuar no puede esperar. Retrasar el cumplimiento supone riesgos serios, especialmente a medida que el HHS planea intensificar las actividades de aplicación en septiembre de 2025 para abordar el bloqueo de información [4]. La ventana para lograr el cumplimiento está cerrándose rápidamente. Estos desarrollos enfatizan una conclusión clave: en 2025, el cumplimiento no solo es esencial, está evolucionando a un ritmo rápido.
Preguntas Frecuentes
¿Cuáles son las principales actualizaciones de la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA de 2025?
Las actualizaciones de 2025 a la Regla de Seguridad de HIPAA marcan un avance importante en el fortalecimiento de la seguridad de los datos y garantizar el cumplimiento. Uno de los cambios más notables es el cambio de salvaguardias "abordables" a obligatorias. Esto significa que cada organización ahora debe implementar estas medidas sin excepciones. Además, los asociados comerciales ahora están obligados a informar directamente las violaciones e incidentes de seguridad a la Oficina de Derechos Civiles (OCR). Otra actualización crítica es el requisito universal de cifrar toda la información de salud protegida electrónica (ePHI), ya sea que se almacene o se transmita.
Las actualizaciones también introducen varias otras medidas esenciales, incluyendo autenticación multifactorial obligatoria, gestión regular de parches, pruebas de penetración rutinarias y análisis de riesgos más detallados. Estas evaluaciones de riesgos están diseñadas para identificar vulnerabilidades y evaluar amenazas potenciales a ePHI. Al alinearse con el Marco de Ciberseguridad de NIST, estas actualizaciones tienen como objetivo abordar los crecientes riesgos planteados por ciberataques como ransomware. En conjunto, estos cambios establecen estándares más estrictos para proteger los datos del paciente y asegurar la responsabilidad, especialmente al compartir datos con terceros.
¿Qué cambios traen los requisitos de auditoría de 2025 a la compartición de datos con terceros en la TI de salud?
Los requisitos de auditoría de 2025 traen regulaciones más estrictas para compartir datos con terceros en la TI de salud. Bajo estas nuevas reglas, las organizaciones deben establecer controles de auditoría detallados y mantener registros completos de cada instancia de acceso y transferencia de datos. Además, los asociados comerciales de terceros ahora deben adherirse a los mismos estándares de seguridad que los proveedores de atención médica, asegurando que la información de salud sensible permanezca protegida.
Estos cambios están diseñados para aumentar la transparencia y la responsabilidad, protegiendo la información de salud protegida electrónica (ePHI) mientras se alinea con las regulaciones federales. Mantenerse al día con estos requisitos es crucial para preservar la confianza y evitar posibles sanciones.
¿Qué pasos deben seguir los desarrolladores de aplicaciones de salud de IA para cumplir con los requisitos de auditoría de 2025?
Para cumplir con los requisitos de auditoría de TI de salud de 2025, los desarrolladores de aplicaciones de salud de IA necesitan una estrategia bien organizada. Aquí se explica cómo comenzar:
Familiarízate con las Regulaciones: Identifica las leyes federales y estatales relevantes para tu aplicación, como HIPAA, la Ley HITECH y regulaciones más recientes centradas en la IA como la AB 489 de California. Si tu aplicación maneja datos transfronterizos, marcos como GDPR también deben estar en tu radar.
Realizar una Evaluación de Riesgos: Identifica vulnerabilidades en tu aplicación - ya sean técnicas, administrativas o físicas. Luego, implementa salvaguardias como cifrado, controles de acceso basado en roles y registros de auditoría. Asigna un oficial de cumplimiento para supervisar estas medidas y asegurarte de que todo se mantenga en camino.
Fortalecer las Relaciones con Proveedores: Usa Acuerdos de Asociados Comerciales (BAAs) para confirmar que los proveedores externos cumplan con tus requisitos de seguridad. Mapea cómo los datos sensibles, como las biométricas o los resultados de laboratorio, se mueven a través de sistemas de terceros para identificar y abordar posibles riesgos.
Compromiso con el Monitoreo y Formación Continuos: Utiliza herramientas para detectar actividad sospechosa, programa auditorías rutinarias y ofrece al personal formación regular sobre protocolos de privacidad y ética de IA.
Antes de lanzar tu aplicación, valida su cumplimiento a través de pruebas funcionales y regulatorias. Asegúrate de que los resultados de IA sean fáciles de entender, estén libres de sesgo y estén claramente etiquetados para que los usuarios sepan que están interactuando con un algoritmo. Después del lanzamiento, mantén el cumplimiento auditando regularmente, actualizando salvaguardias cada vez que cambien los sistemas y manteniendo registros exhaustivos para cumplir con los requisitos de auditoría. Estos pasos no solo protegen los datos del paciente, sino que también ayudan a ofrecer un cuidado personalizado y seguro.
Entradas de Blog Relacionadas
Finalmente toma el control de tu salud

Finalmente toma el control de tu salud

Finalmente toma el control de tu salud





